Low FODMAP Cereal: 12 Best Gut-Friendly Options

Finding a low FODMAP cereal doesn't have to mean sacrificing your morning routine. With two-thirds of Americans experiencing digestive issues and nearly 1 billion people worldwide living with IBS, choosing the right breakfast cereal can make a real difference in how you feel throughout the day. For a deeper dive into the science behind FODMAPs and digestive health, see this recent clinical review.
Key Takeaways
- Many cereals can be low FODMAP, such as Rice Krispies, Corn Flakes, and plain oats.
- Choosing cereals made from rice, corn, or oats helps maintain a low FODMAP diet.
- It is important to avoid wheat, high fructose sweeteners, and large portion sizes in cereals.
- Low FODMAP cereals can support digestive health for people with IBS or other digestive issues.
- Selecting the right breakfast cereal can positively impact how you feel throughout the day.
Table of Contents
- What is the Low FODMAP Diet?
- Why Choosing Low FODMAP Cereal Can Be a Challenge
- How to Identify Low FODMAP-Friendly Cereals
- 7 Dietitian & Expert Recommended Low FODMAP Cereals
- Top 7 Low FODMAP Hot Breakfast Cereals
- How to Build a Balanced Low FODMAP Breakfast Bowl
- 5 Alternative Low FODMAP Breakfast Ideas
- Resources for Low FODMAP Diet Success
- Recap and Next Steps
The good news? There are plenty of delicious, gut-friendly cereal options that won't trigger digestive discomfort. From classic Rice Krispies to hearty oat-based cereals, you can enjoy a satisfying breakfast without the bloating, gas, or stomach pain that often comes with high FODMAP foods.
We'll walk you through everything you need to know about selecting cereals that support easier digestion, plus share expert-recommended brands and practical tips for building balanced, flavorful breakfast bowls that work for your gut. For more breakfast inspiration, check out our Low FODMAP Recipes blog for creative morning meal ideas.
What is the Low FODMAP Diet?
Understanding FODMAPs
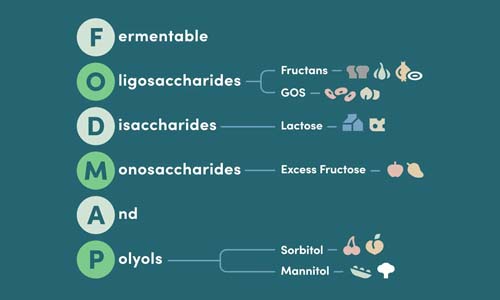
FODMAP stands for Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols – a group of short-chain carbohydrates that can be difficult for some people to digest properly.
Key Point: FODMAPs aren't inherently "bad" foods, but they can trigger digestive symptoms in sensitive individuals by drawing water into the intestines and fermenting in the gut.
When FODMAPs reach the large intestine undigested, they become food for gut bacteria. This fermentation process can cause:
- Excessive gas and bloating
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Nausea and digestive discomfort
The low FODMAP approach is particularly beneficial for people with IBS, SIBO (Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth), and other functional digestive disorders. Research shows that up to 75% of people with IBS experience significant symptom improvement when following a low FODMAP diet. For more on the effectiveness of this approach, see this peer-reviewed study.
Phases of the Low FODMAP Diet
The low FODMAP diet isn't meant to be a permanent restriction. It's designed as a three-phase process:
- Elimination Phase (2-6 weeks)
- Remove high FODMAP foods to allow your digestive system to calm down and symptoms to improve.
- Reintroduction Phase (6-10 weeks)
- Systematically reintroduce FODMAP groups one at a time to identify your personal triggers and tolerance levels.
- Personalization Phase (ongoing)
- Create a long-term eating plan that includes as many foods as possible while avoiding your specific triggers.
"The goal isn't to follow a low FODMAP diet forever – it's to understand your body's unique needs and create a sustainable way of eating that supports your digestive health," explains the team at Monash University, who developed the low FODMAP protocol.
Why Choosing Low FODMAP Cereal Can Be a Challenge
Common High FODMAP Ingredients in Breakfast Cereals
Many popular cereals contain ingredients that can trigger digestive symptoms. Here's what to watch out for:
High FODMAP Grains: Wheat, rye, and barley are common cereal bases that contain fructans – a type of oligosaccharide that can cause bloating and gas in sensitive individuals.
Beyond grains, cereals often contain problematic sweeteners:
- Honey and high fructose corn syrup: These contain excess fructose, which can be difficult to absorb
- Sugar alcohols: Sorbitol, mannitol, and xylitol are polyols that can cause digestive upset
- Inulin and chicory root: Often added as fiber sources, these are high in fructans
Even seemingly healthy additions like dried fruits can be problematic. Raisins, dates, and dried apples are all high FODMAP and commonly found in granola-style cereals.
The Importance of Label-Checking and Portion Size
Here's the thing: FODMAP content isn't just about ingredients – portion size matters tremendously. Some cereals that are high FODMAP in large servings can be perfectly fine in smaller amounts.
Are Cheerios low FODMAP? Yes, but only in portions of ½ cup or less. Larger servings contain enough wheat to trigger symptoms in sensitive individuals.
This is why reading labels carefully is crucial. Look for:
- Serving size information
- Primary grain ingredients (first few ingredients listed)
- Types of sweeteners used
- Added fiber sources
The Monash University FODMAP app provides tested portion sizes for many commercial cereals, taking the guesswork out of breakfast planning.
How to Identify Low FODMAP-Friendly Cereals
Best Low FODMAP Cereal Ingredients
When shopping for low FODMAP cereal, focus on these gut-friendly base ingredients that provide excellent nutrition without triggering digestive symptoms:
Top Low FODMAP Grains: Rice, oats, corn, buckwheat, quinoa, millet, and amaranth are naturally gentle on digestion and form the foundation of most gut-friendly cereals.
- Rice-based cereals: Rice Krispies, puffed rice, and rice flakes are excellent choices with minimal processing
- Corn cereals: Corn flakes and puffed corn provide satisfying crunch without wheat-based fructans
- Oat cereals: Rolled oats, steel-cut oats, and oat bran offer fiber and protein for sustained energy
- Ancient grains: Buckwheat, quinoa, millet, and amaranth add variety and nutritional density
These ingredients work because they're naturally low in FODMAPs and don't contain the problematic compounds found in wheat, rye, and barley. Rice and corn, in particular, are considered some of the safest options for people with sensitive digestive systems. For more ideas on incorporating these grains into your meals, explore our simple low FODMAP gourmet risotto recipe.
Cereal Ingredients to Avoid
Certain ingredients consistently show up in cereals and can trigger digestive discomfort. Here's what to skip:
High FODMAP Red Flags: If you see wheat, rye, barley, honey, high fructose corn syrup, inulin, or chicory root in the first few ingredients, that cereal is likely high FODMAP.
- Gluten-containing grains
- Wheat, rye, and barley contain fructans that can cause bloating and gas in sensitive individuals
- Problematic sweeteners
- Honey, agave, high fructose corn syrup, and sugar alcohols like sorbitol and mannitol
- Added fiber sources
- Inulin and chicory root are commonly added for fiber but are high in fructans
- Excess dried fruits
- Raisins, dates, and dried apples contain concentrated fructose and can overwhelm your digestive system
Safe Sweeteners and Additions
You don't have to sacrifice sweetness when choosing low FODMAP cereals. These sweeteners and additions are generally well-tolerated:
Are Honey Nut Cheerios low FODMAP? No, Honey Nut Cheerios contain honey, which is high FODMAP due to excess fructose. Stick to plain Cheerios in ½ cup portions instead.
- Maple syrup: Pure maple syrup is low FODMAP and adds natural sweetness
- Cane sugar: Regular sugar is well-tolerated in normal amounts
- Rice malt syrup: A gentle alternative that's naturally low FODMAP
- Cocoa/dark chocolate: Pure cocoa powder is low FODMAP and adds rich flavor
The key is moderation – even low FODMAP sweeteners can cause issues in very large quantities.
7 Dietitian & Expert Recommended Low FODMAP Cereals

Monash Certified and Widely Available
These cereals have been tested by Monash University researchers and are readily available in most grocery stores:
Quick Reference: All Kellogg's rice-based and corn-based cereals listed below are considered low FODMAP in standard serving sizes (typically ¾ to 1 cup).
Kellogg's Rice Krispies
The classic puffed rice cereal that's been a breakfast staple for generations. Made with simple ingredients – rice, salt, and minimal processing – Rice Krispies provide a satisfying crunch without digestive upset.
Kellogg's Frosted Krispies
All the benefits of regular Rice Krispies with a touch of sweetness from sugar rather than problematic sweeteners. The frosting uses low FODMAP ingredients, making this a gut-friendly option for those with a sweet tooth.
Kellogg's Cocoa Krispies
Chocolate lovers can enjoy this cocoa-flavored version without worry. The cocoa powder is naturally low FODMAP, and the rice base remains gentle on digestion.
Kellogg's Corn Flakes
A timeless choice made from corn, salt, and minimal additives. Corn Flakes offer a classic cereal experience with excellent digestive tolerance and a satisfying crunch that holds up well in milk.
Kellogg's Crispix
This unique cereal combines rice and corn in a distinctive lattice shape, offering variety in texture while maintaining low FODMAP status. It's particularly good for those who want something different from standard flakes or puffs.
Kellogg's Frosted Flakes
The beloved "They're Gr-r-reat!" cereal uses corn as its base with sugar frosting rather than high FODMAP sweeteners. Tony the Tiger's favorite remains a gut-friendly option for sweet cereal lovers.
Kellogg's Strawberry Rice Krispies
A fruity twist on the classic, using natural strawberry flavoring that doesn't contain high FODMAP fruit concentrates. This variety adds color and flavor variety to your breakfast routine.
General Mills Options (Portion-Dependent)
These cereals are low FODMAP when consumed in the specified portion sizes:
"Portion control is crucial with wheat-containing cereals like Cheerios. The ½ cup limit isn't arbitrary – it's based on laboratory testing of FODMAP content at different serving sizes," notes FODMAP research from Monash University.
- Rice Chex: Made from rice, this cereal is naturally low FODMAP in standard servings
- Corn Chex: Corn-based option that's well-tolerated and provides satisfying crunch
- Cheerios: Limited to ½ cup servings due to wheat content, but safe in controlled portions
Other Notable Brand Options
Beyond the mainstream brands, several specialty companies offer excellent low FODMAP cereal options that prioritize clean ingredients and digestive wellness:
Organic Advantage: Many specialty brands use organic ingredients, which means no synthetic pesticides or GMOs – a bonus for those prioritizing clean eating alongside digestive health.
- Annie's Homegrown Organic Cocoa Bunnies: Organic corn-based cereal with cocoa that's naturally low FODMAP
- Arrowhead Organic Maple Buckwheat Flakes: Buckwheat provides protein and fiber with gentle maple sweetening
- Barbara's Puffins (Peanut Butter varieties): Corn-based with natural peanut butter flavoring
- EnviroKidz Panda Puffs and Gorilla Munch: Organic, fun-shaped cereals made from rice and corn
- Nature's Path Crispy Rice: Simple, organic rice cereal without unnecessary additives
These brands often cost more than mainstream options, but they typically offer cleaner ingredient profiles and organic certification – important factors for our customers who prioritize both digestive wellness and ingredient transparency. For more ways to enjoy low FODMAP meals throughout the day, visit our FODMAP blog for tips and recipes.
Top 7 Low FODMAP Hot Breakfast Cereals
Hot cereals offer comforting warmth and sustained energy, making them perfect for cooler mornings or when you need lasting satiety. Here are the most reliable options for sensitive digestive systems:
Hot Cereal Benefits: Warm cereals are often easier to digest than cold options and provide better satiety through slower eating and increased fiber absorption.
Plain Rolled Oats (Unflavored)
The gold standard for hot breakfast cereals, plain rolled oats are naturally low FODMAP and provide excellent fiber for digestive health. Oats contain beta-glucan fiber, which supports healthy gut bacteria and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Serving Size Matters: Stick to ½ cup of dry oats per serving. Larger portions may contain enough fructans to trigger symptoms in very sensitive individuals.
Steel-Cut Oats
These minimally processed oats take longer to cook but offer superior texture and nutty flavor. Steel-cut oats have a lower glycemic index than rolled oats, providing steadier energy release throughout the morning.
Oat Bran
Concentrated fiber from oat processing, oat bran cooks quickly and provides exceptional digestive benefits. It's particularly helpful for those dealing with constipation-predominant IBS symptoms.
Buckwheat Groats
Despite the name, buckwheat contains no wheat and is naturally gluten-free. These hearty groats provide complete protein and have a unique, earthy flavor that's satisfying and filling.
Rice Bran or Cream of Rice
Ultra-gentle options that cook quickly and provide smooth, comforting texture. Rice-based hot cereals are excellent for those with multiple food sensitivities or during digestive flare-ups.
Grits (Corn-Based, Unflavored)
Traditional Southern comfort food made from ground corn. Plain grits are naturally low FODMAP and provide a creamy, satisfying base that pairs well with low FODMAP toppings.
Puffed Amaranth or Millet Porridge
Ancient grains that offer variety and exceptional nutrition. Both amaranth and millet are complete proteins and provide minerals often lacking in refined cereals.
"Hot cereals allow for better portion control and slower eating, which can improve digestion and reduce bloating. The warm temperature also helps activate digestive enzymes," notes digestive health research.
Recommended Brands for Hot Cereals
These brands consistently deliver quality hot cereals with clean ingredient profiles:
- Bob's Red Mill Mighty Tasty Hot Cereal: Blend of whole grains that's naturally low FODMAP
- Bob's Red Mill Creamy Buckwheat: Smooth-cooking buckwheat that's gentle on digestion
- Ancient Harvest Quinoa Flakes: Quick-cooking quinoa option with complete protein
- Arrowhead Gluten Free Rice & Shine: Creamy rice cereal that's ultra-gentle
- Cream of Rice (Nabisco): Classic option that's widely available and reliably low FODMAP
How to Build a Balanced Low FODMAP Breakfast Bowl

Creating a nutritious breakfast goes beyond just choosing the right cereal – it's about combining ingredients that support both digestive wellness and overall nutrition. For a savory, protein-rich breakfast, try our Ultimate Low FODMAP Frittata recipe as a delicious alternative.
Milk & Non-Dairy Alternatives
Regular cow's milk contains lactose, a disaccharide that can trigger digestive symptoms in sensitive individuals. Here are your best alternatives:
Why avoid regular milk? Regular cow's milk contains lactose, which is high FODMAP. Many people with IBS also have lactose intolerance, making milk a double trigger for digestive discomfort.
- Lactose-free cow's milk
- Maintains the taste and nutrition of regular milk without the digestive issues
- Unsweetened almond milk
- Low FODMAP when made from almonds rather than whole nuts; check labels for added sweeteners
- Soy milk (from soy protein isolate)
- Choose versions made from soy protein isolate rather than whole soybeans for better tolerance
- Rice milk (in moderation)
- Naturally sweet and gentle, but higher in carbohydrates than other alternatives
Low FODMAP Toppings & Mix-Ins
Transform your basic cereal into a nutritional powerhouse with these carefully chosen additions:
Portion-Controlled Fruits: Stick to ½ cup of strawberries, ¾ cup of blueberries, or one small unripe banana to stay within low FODMAP limits.
Fresh Fruit Options
- Unripe banana: Provides potassium and natural sweetness without excess fructose
- Strawberries: High in vitamin C and antioxidants, naturally low FODMAP
- Blueberries: Packed with antioxidants and fiber in appropriate portions
- Kiwi fruit: Excellent source of vitamin C and digestive enzymes
Seeds and Nuts
- Chia seeds: Provide omega-3 fatty acids and soluble fiber
- Ground flaxseed: Supports digestive health and provides healthy fats
- Pumpkin seeds: Rich in magnesium and zinc
- Walnuts (small amounts): Provide healthy fats and protein
Fiber and Digestion Tips
Fiber is crucial for digestive health, but the type and amount matter significantly for those with sensitive systems:
Hydration is Key: Aim for 1.5–2L of water daily, especially when increasing fiber intake. Proper hydration helps fiber work effectively and prevents constipation.
Start with smaller portions of high-fiber cereals and gradually increase as your digestive system adapts. This approach helps prevent bloating and gas while still providing the digestive benefits of fiber.
5 Alternative Low FODMAP Breakfast Ideas
While cereal is convenient, variety keeps breakfast interesting and ensures you're getting diverse nutrients. Here are creative alternatives that maintain digestive wellness:
Pancakes & Waffles
Made with low FODMAP flours like buckwheat, rice, or oat flour, these weekend treats can be gut-friendly. Use lactose-free milk and top with maple syrup and fresh berries for a satisfying morning meal.
Smoothie Bowls
Blend lactose-free milk with low FODMAP fruits and pour into a bowl. Top with seeds, nuts, and additional fruit for a Instagram-worthy breakfast that's gentle on digestion.
Egg-Based Dishes
Eggs are naturally low FODMAP and provide complete protein. Scrambled, boiled, or poached eggs pair perfectly with low FODMAP toast or roasted vegetables for a savory breakfast option.
Savory Grain Bowls
Cooked quinoa, rice, or millet topped with herbs, seeds, and vegetables creates a satisfying breakfast that breaks away from traditional sweet morning meals.
Breakfast Bars & Energy Bites
Homemade options using oats, peanut butter, and low FODMAP mix-ins provide grab-and-go convenience without the questionable ingredients found in many commercial bars.
"Breakfast variety ensures you're getting different nutrients and prevents food boredom, which can lead to poor dietary adherence. Mix cereals with other options throughout the week," recommend nutrition experts.
Resources for Low FODMAP Diet Success
Successfully managing a low FODMAP diet requires ongoing education and support. Here are the most valuable resources to ensure your breakfast choices – and overall diet – support your digestive wellness goals:
The Monash FODMAP App
This research-backed app from Monash University provides the most up-to-date FODMAP information available. It includes portion sizes, traffic light ratings, and regular updates as new foods are tested.
Dietitian Support
Consider consulting a FODMAP-trained registered dietitian, especially during the elimination and reintroduction phases. Professional guidance helps ensure nutritional adequacy while managing symptoms effectively.
Community & Online Forums
Connect with others following the low FODMAP diet through online communities where you can share recipes, troubleshoot challenges, and find support from people who understand your journey.
Remember: The low FODMAP diet is a tool for identifying triggers, not a permanent restriction. Most people can reintroduce many foods after the elimination phase.
Recap and Next Steps
Choosing the right low FODMAP cereal doesn't mean sacrificing flavor or nutrition. With options ranging from classic Rice Krispies to specialty organic varieties, you can enjoy satisfying breakfasts while supporting your digestive health.
Key Takeaways: Focus on rice, corn, and oat-based cereals, check portion sizes for wheat-containing options like Cheerios, and build complete breakfast bowls with low FODMAP toppings and appropriate milk alternatives.
Start by trying one or two new low FODMAP cereals this week, and pay attention to how your body responds. Remember that everyone's tolerance levels are different, and what works for others may need adjustment for your specific needs.
The most important step is beginning – your digestive wellness journey starts with simple changes like choosing the right breakfast cereal. From there, you can build confidence and expand your low FODMAP repertoire to include the full range of delicious, gut-friendly foods available.
Check out our Low Fodmap Bundles
Frequently Asked Questions
What cereals can you eat on low FODMAP?
On a low FODMAP diet, cereals made from low FODMAP grains like rice, oats, corn, and quinoa are good choices. Look for cereals that contain simple, recognizable ingredients without high FODMAP additives such as honey, inulin, or high-fructose corn syrup. Plain oatmeal, puffed rice, corn flakes without added high FODMAP sweeteners, and certain gluten-free cereals made with quinoa or rice often work well.
What breakfast cereals can I eat with IBS?
If you have IBS, choosing cereals free from common triggers like wheat, rye, barley, and high FODMAP sweeteners is key. Opt for low FODMAP grains like oats and rice-based cereals, and check labels for no added onion or garlic powders. Simple, clean-label options with minimal ingredients help reduce the risk of flare-ups while still offering satisfying texture and flavor.
Can I have Cheerios on FODMAP diet?
Cheerios are made primarily from oats, which are low FODMAP in moderate portions, so they can fit into a low FODMAP diet if eaten in controlled amounts. However, some varieties contain added ingredients like honey or fruit pieces that may increase FODMAP content, so it’s best to choose original Cheerios and watch your serving size to avoid digestive discomfort.
Are frosted flakes fodmap friendly?
Frosted flakes typically contain added sugars and sweeteners that can be high FODMAP, such as high fructose corn syrup or honey, which may trigger symptoms. Additionally, the corn base itself is low FODMAP, but the frosting coating can make these cereals less gut-friendly. For better digestive comfort, it’s best to avoid frosted flakes or look for unsweetened corn-based cereals.
What cereal does not cause bloating?
Cereals made from low FODMAP grains like rice flakes, plain oats, and puffed quinoa usually cause less bloating because they avoid fermentable sugars that feed gut bacteria excessively. Choosing cereals with no added high FODMAP ingredients and keeping portion sizes moderate helps maintain digestive comfort and reduces the chance of bloating.
Is special K cereal low FODMAP?
Special K cereals often contain wheat and other ingredients high in FODMAPs, making them generally unsuitable for a low FODMAP diet. Some varieties may also have added sweeteners or flavorings that increase FODMAP content. If you’re managing IBS or gut sensitivities, it’s safer to choose cereals made from low FODMAP grains like oats or rice instead.