Is Pineapple Low FODMAP? Your Complete Guide

Is Pineapple Low FODMAP? Your Essential Guide
If you're managing IBS or following a low FODMAP diet, you've probably wondered about your favorite fruits—including the sweet, tropical appeal of pineapple. The good news? Pineapple can absolutely be part of your low FODMAP lifestyle, as long as you stick to the right portions. For a broader overview of FODMAP-friendly foods and tips, visit our FODMAP blog.
Key Takeaways
- Pineapple is low FODMAP when consumed in appropriate portions.
- Fresh pineapple is low FODMAP up to 140g (1 cup).
- Canned pineapple in juice is low FODMAP up to 90-97g.
- Larger portions of pineapple may trigger digestive symptoms in people with IBS.
- Pineapple can be included in a low FODMAP diet if portion sizes are carefully managed.
Table of Contents
- Is Pineapple Low FODMAP? Your Essential Guide
- What Is the Low FODMAP Diet?
- Understanding FODMAPs in Fruits
- Spotlight on Pineapple: Is It Low FODMAP?
- Health Benefits of Pineapple
- How to Enjoy Pineapple on a Low FODMAP Diet
- Tips for Success on a Low FODMAP Diet
- Exploring Other Low FODMAP Fruits
- Building Your Low FODMAP Lifestyle
- Conclusion
With nearly 1 billion people worldwide living with IBS and two-thirds of Americans experiencing digestive issues, understanding which foods support gut health has never been more important. Fruits can be particularly tricky territory since many contain FODMAPs that trigger bloating, gas, and digestive discomfort. For a comprehensive guide to the low FODMAP diet, see this Johns Hopkins Medicine resource.
Key Fact: Fresh pineapple is low FODMAP up to 140g (about 1 cup), making it one of the more generous fruit servings allowed on the diet.
We'll break down everything you need to know about enjoying pineapple while keeping your digestion comfortable—from portion sizes to different forms of pineapple, plus how it compares to other popular fruits like raspberries, cherries, and dragon fruit. For more on delicious ways to enjoy low FODMAP meals, check out our low FODMAP recipes blog.
What Is the Low FODMAP Diet?
 is grapefruit low fodmap">
is grapefruit low fodmap">
Definition and Purpose
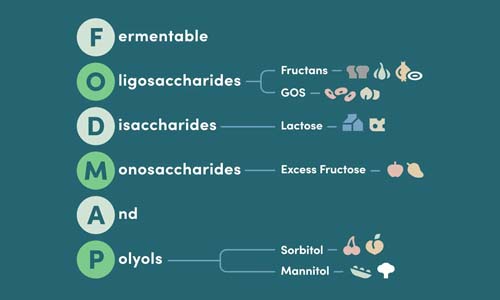
FODMAP stands for Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols—a group of short-chain carbohydrates that can be poorly absorbed in the small intestine. When these compounds reach the large intestine, they ferment and can cause uncomfortable symptoms in sensitive individuals. For a deeper dive into the science behind FODMAPs, you can also read this Cleveland Clinic overview.
The low FODMAP diet isn't about permanent restriction—it's a systematic approach to identify your personal trigger foods through elimination and careful reintroduction.
Here's how FODMAPs can affect digestion:
- Fermentation: Gut bacteria feed on unabsorbed FODMAPs, producing gas
- Water retention: FODMAPs draw water into the intestines, potentially causing diarrhea
- Symptom triggers: This process can lead to bloating, cramping, and irregular bowel movements
Who Should Consider the Diet?
The low FODMAP approach is primarily recommended for people with:
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Research shows 70-80% of IBS patients experience symptom improvement on a low FODMAP diet
- Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth (SIBO)
- Reducing fermentable carbohydrates can help manage bacterial overgrowth symptoms
- Other functional digestive disorders
- Some people with unexplained digestive symptoms find relief through FODMAP management
Important: While we provide evidence-based information about low FODMAP foods, working with a registered dietitian ensures you're following the diet safely and effectively, especially during the reintroduction phase.
Understanding FODMAPs in Fruits
Common High vs Low FODMAP Fruits
Fruits contain different types of FODMAPs, which explains why some trigger symptoms while others don't. The main culprits in high FODMAP fruits are excess fructose and polyols (sugar alcohols like sorbitol and mannitol).
High FODMAP Fruits to Limit:
- Apples (high in excess fructose and sorbitol)
- Pears (contain sorbitol)
- Watermelon (excess fructose)
- Mangoes (excess fructose)
- Cherries (contain sorbitol and excess fructose)
- Dried fruits (concentrated FODMAPs)
Low FODMAP Fruits to Enjoy:
- Grapes (balanced fructose-to-glucose ratio)
- Strawberries (low in FODMAPs overall)
- Kiwi (well-tolerated in standard portions)
- Oranges (citrus fruits are generally low FODMAP)
- Blueberries (antioxidant-rich and gut-friendly)
- Pineapple (low FODMAP in appropriate portions)
What about those other fruits you might be curious about?
- Are raspberries low FODMAP? Yes, raspberries are low FODMAP up to 60g (about 1/2 cup)
- Are cherries low FODMAP? No, cherries are high FODMAP and should be avoided during elimination
- Is dragon fruit low FODMAP? Yes, dragon fruit is considered low FODMAP in typical serving sizes
- Is grapefruit low FODMAP? Yes, grapefruit is low FODMAP up to 80g (about 1/2 medium fruit)
Why Portion Sizes Matter
Here's something crucial that many people miss: the dose makes the difference. A fruit might be low FODMAP in a small serving but become high FODMAP when you eat too much.
"Even low FODMAP fruits can trigger symptoms if you eat large portions or consume multiple servings close together. We recommend spacing fruit servings at least 3 hours apart to allow proper digestion." - Based on Monash University FODMAP research
This portion-dependent nature is exactly why pineapple makes such a great choice—its low FODMAP threshold is relatively generous compared to many other fruits, giving you more flexibility in your meals and snacks. For more on the science and practical tips, explore our Learn blog section.
Spotlight on Pineapple: Is It Low FODMAP?
Quick Answer: Yes, fresh pineapple is low FODMAP up to 140g (1 cup). Canned pineapple in juice is low FODMAP up to 90-97g, while dried pineapple should be avoided as it's high FODMAP.
Fresh Pineapple FODMAP Content
Based on testing by Monash University—the gold standard for FODMAP research—fresh pineapple is low FODMAP up to 140g per serving. This translates to about 1 cup of fresh pineapple chunks, which is actually quite generous compared to many other fruits. For a detailed breakdown, see this IBS Dietitian article on pineapple and FODMAPs.
The 140g serving size makes pineapple one of the more flexible low FODMAP fruits, allowing you to enjoy a satisfying portion without triggering digestive symptoms.
Here's what happens when you exceed this amount:
- Moderate FODMAP load: Portions between 140-280g may contain moderate levels of oligo-fructans
- Individual tolerance: Some people may tolerate slightly larger portions, while others are more sensitive
- Cumulative effect: Eating multiple fruit servings throughout the day can add up to trigger symptoms
Canned Pineapple and Other Forms
Not all pineapple is created equal when it comes to FODMAP content. Processing and added ingredients can significantly impact how much you can safely enjoy.
- Canned Pineapple in Juice
- Low FODMAP up to 90-97g (roughly 1/2 cup). The natural juice doesn't add significant FODMAPs, but the smaller portion size accounts for the concentrated nature of canned fruit.
- Canned Pineapple in Syrup
- Best to limit or avoid during the elimination phase. Added sugars and syrups can increase the FODMAP load and may contain high fructose corn syrup.
- Dried Pineapple
- High FODMAP and should be avoided during elimination. The dehydration process concentrates the natural sugars, making even small portions problematic for sensitive individuals.
- Pineapple Juice
- Exercise caution—concentrated fruit juices often contain higher FODMAP levels than whole fruit, and specific testing data is limited.
Quick Reference Table
| Pineapple Form | Low FODMAP Serving Size | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh pineapple | 140g (1 cup chunks) | Most generous serving size |
| Canned in juice | 90-97g (~1/2 cup) | Drain juice before measuring |
| Canned in syrup | Limit or avoid | Added sugars increase FODMAP load |
| Dried pineapple | Avoid | High FODMAP due to concentration |
| Pineapple juice | Use caution | Limited testing data available |
Measuring Tip: A kitchen scale is your best friend for accurate portions. If you don't have one, 140g of fresh pineapple is roughly equivalent to 1 cup of chunks or 2-3 rings of fresh pineapple.
Health Benefits of Pineapple

Nutritional Highlights
Beyond being low FODMAP, pineapple brings impressive nutritional value to your diet. This tropical fruit is particularly rich in vitamin C, providing over 100% of your daily needs in a single cup.
Key Nutrients in 1 Cup Fresh Pineapple:
- Vitamin C: 78.9mg (131% daily value) - supports immune function and collagen production
- Manganese: 0.9mg (76% daily value) - essential for bone health and metabolism
- Dietary Fiber: 2.3g - supports digestive health and regularity
- Bromelain: Natural enzyme with anti-inflammatory properties
- Thiamine (B1): Supports energy metabolism
Digestive Benefits Relevant to IBS
Pineapple contains bromelain, a proteolytic enzyme that may support protein digestion. While research is ongoing, some studies suggest bromelain may help reduce inflammation and support overall digestive comfort.
"Including a variety of low FODMAP fruits like pineapple ensures you're getting diverse nutrients while managing IBS symptoms. The key is sticking to tested portion sizes and listening to your body's responses."
The natural fiber in pineapple can also support healthy digestion when consumed in appropriate amounts. Unlike high FODMAP fruits that may trigger symptoms, pineapple's fiber content works with your digestive system rather than against it.
How to Enjoy Pineapple on a Low FODMAP Diet
Meal and Snack Ideas
The beauty of pineapple's generous 140g serving size is that it opens up numerous culinary possibilities. Here are some delicious ways to incorporate this tropical fruit into your low FODMAP lifestyle. For more recipe inspiration, browse our low FODMAP recipes blog.
Tropical Chicken Salad
Combine grilled chicken breast with fresh pineapple chunks, mixed greens, and a light vinaigrette made with olive oil and lemon juice. The pineapple adds natural sweetness and pairs beautifully with the savory chicken. For a flavorful dressing, try our Low FODMAP French Vinaigrette recipe.
Pineapple-Ginger Smoothie
Blend your 140g portion of pineapple with fresh ginger, spinach, and lactose-free yogurt. The ginger adds digestive support while the pineapple provides tropical flavor and natural sweetness.
Grilled Pineapple Side Dish
Grill pineapple rings and serve alongside grilled chicken or fish. The caramelization brings out the natural sugars while keeping within your FODMAP limits. For more protein ideas, check out our Low FODMAP Miso Salmon recipe.
Tips for Including Pineapple
Success with pineapple on a low FODMAP diet comes down to smart planning and mindful eating:
- Measure portions: Always weigh or measure your pineapple to stay within the 140g limit
- Space out servings: Wait at least 3 hours between fruit servings to allow proper digestion
- Pair strategically: Combine pineapple with low FODMAP proteins or vegetables for balanced meals
- Fresh is best: Opt for fresh pineapple when possible for the most generous serving size
- Read labels: Check processed foods containing pineapple for hidden high FODMAP ingredients
What fruits are low FODMAP? Low FODMAP fruits include pineapple (140g), strawberries (140g), grapes (150g), oranges (130g), kiwi (140g), blueberries (90g), raspberries (60g), and dragon fruit in typical portions. Always check serving sizes as they vary by fruit.
Tips for Success on a Low FODMAP Diet
Portion Control and Meal Timing
The difference between enjoying pineapple comfortably and experiencing symptoms often comes down to timing and portions. Here's how to maximize your success:
The 3-Hour Rule: Space fruit servings at least 3 hours apart to prevent FODMAP stacking—where multiple low FODMAP foods consumed together create a high FODMAP load.
- Morning strategy: Enjoy your 140g pineapple serving with breakfast, then wait until afternoon for your next fruit
- Meal pairing: Combine pineapple with protein or healthy fats to slow digestion and improve tolerance
- Label vigilance: Check processed foods for hidden FODMAPs like high fructose corn syrup or excess fructose
- Kitchen scale investment: Accurate measuring prevents accidental overconsumption
Pro Tip: Pre-portion your pineapple into 140g containers when you buy it fresh. This removes guesswork and makes healthy snacking effortless.
Monitoring Symptoms and Reintroduction
Even with low FODMAP foods like pineapple, individual tolerance can vary. The elimination phase is just the beginning—reintroduction helps you understand your personal triggers and expand your dietary options.
"Keep a detailed food and symptom diary during both elimination and reintroduction phases. This data becomes invaluable for identifying patterns and building your personalized low FODMAP lifestyle."
During reintroduction, you might test larger portions of pineapple or different forms to understand your individual limits. Some people tolerate up to 200g of fresh pineapple, while others find 100g is their sweet spot.
Use Trusted Tools and Resources
Navigating the low FODMAP diet successfully requires reliable information. The Monash University FODMAP app remains the gold standard for up-to-date serving sizes and testing results.
Essential Low FODMAP Resources:
- Monash FODMAP App: Real-time updates on food testing and serving sizes
- Registered Dietitian: Professional guidance for complex cases or ongoing struggles
- Food diary apps: Track symptoms, meals, and patterns over time
- Gourmend's recipe tools: Convert favorite recipes to low FODMAP versions
Exploring Other Low FODMAP Fruits

Are raspberries low FODMAP? Yes, raspberries are low FODMAP up to 60g (about 1/2 cup). They're lower in serving size compared to pineapple but offer excellent antioxidants and fiber for digestive health.
Raspberries and Dragon Fruit
While pineapple offers one of the more generous low FODMAP serving sizes, other fruits provide variety and unique nutritional benefits. For a creative way to enjoy berries, try our Ultimate Low FODMAP Frittata recipe.
- Raspberries (60g serving)
- Lower serving size than pineapple but packed with antioxidants and fiber. Perfect for adding to yogurt or smoothies without overwhelming your FODMAP budget.
- Dragon Fruit (typical serving)
- Is dragon fruit low FODMAP? Yes, dragon fruit is generally well-tolerated in normal serving sizes, though specific Monash testing data is limited. Start with smaller portions during elimination.
Are cherries low FODMAP? Fresh cherries are high FODMAP and should be avoided during elimination due to excess fructose and sorbitol content. However, you can enjoy small amounts of sour cherries (about 5 cherries or 45g).
Citrus Options and Grapefruit
Citrus fruits generally perform well on the low FODMAP diet, offering vitamin C and bright flavors without digestive distress:
| Citrus Fruit | Low FODMAP Serving | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Grapefruit | 130g (1/2 large fruit) | High vitamin C, supports immune function |
| Orange | 130g (1 medium) | Folate, potassium, natural sweetness |
| Lemon/Lime | Unlimited (juice/zest) | Flavor enhancement without FODMAP load |
Is grapefruit low FODMAP? Yes, grapefruit is low FODMAP up to 130g per serving. This citrus fruit pairs excellently with savory salads and provides a refreshing contrast to richer dishes.
Building Your Low FODMAP Lifestyle
Strategic Meal Planning
Success with low FODMAP eating extends beyond individual foods like pineapple—it's about creating sustainable meal patterns that support both digestive comfort and nutritional needs.
Weekly Fruit Planning Strategy:
- Monday/Wednesday/Friday: Pineapple-based breakfast or snacks
- Tuesday/Thursday: Citrus fruits for vitamin C variety
- Weekend: Berry combinations for antioxidant diversity
- Always: Leave 3+ hours between fruit servings
This rotation ensures you're getting diverse nutrients while respecting FODMAP limits and preventing food boredom—a common challenge in restrictive diets.
Kitchen Setup for Success
Having the right tools and ingredients makes low FODMAP cooking effortless rather than overwhelming:
- Digital kitchen scale: Essential for accurate portion control
- Glass storage containers: Pre-portion fruits and vegetables for grab-and-go convenience
- Quality broths: Keep Gourmend's low FODMAP broths on hand for quick, flavorful meal bases
- Herb garden: Fresh chives, basil, and other low FODMAP herbs elevate simple dishes
Stock Smart: Our organic, low FODMAP broths use chives and leek greens instead of onions, providing rich umami flavor without digestive triggers. They're perfect for cooking grains, making soups, or deglazing pans.
Conclusion
Pineapple absolutely can be part of your low FODMAP lifestyle—and with its generous 140g serving size, it's one of the more flexible fruits you can enjoy. The key is understanding the differences between fresh, canned, and processed forms, and respecting portion sizes that support your digestive comfort.
Remember: Fresh pineapple offers the largest low FODMAP serving at 140g, while canned varieties require smaller portions. Always avoid dried pineapple during elimination phases.
Beyond just being "allowed" on the diet, pineapple brings genuine nutritional value—vitamin C for immune support, manganese for bone health, and bromelain for potential digestive benefits. When combined with other low FODMAP fruits and strategic meal timing, pineapple helps create the dietary variety that makes this therapeutic approach sustainable long-term.
The low FODMAP diet doesn't have to mean sacrificing flavor or satisfaction. With nearly 1 billion people worldwide managing IBS symptoms, understanding which foods support rather than trigger digestive comfort becomes a powerful tool for reclaiming food freedom.
"Success with low FODMAP eating comes from focusing on abundance rather than restriction. Pineapple exemplifies this—offering tropical flavor, solid nutrition, and digestive peace of mind in one delicious package."
Whether you're new to the low FODMAP approach or fine-tuning your long-term strategy, pineapple represents the kind of win-win ingredient that makes this journey both effective and enjoyable. Measure your portions, space your servings, and savor every tropical bite with confidence.
Check out our Low Fodmap Bundles
Frequently Asked Questions
Is pineapple ok for IBS?
Pineapple can be a good fruit choice for many people with IBS because it’s low FODMAP in moderate amounts. It offers natural sweetness and digestive enzymes like bromelain, which may help break down proteins and ease digestion. However, portion size matters, and eating too much can lead to symptoms for some.
How much pineapple can you eat on a low FODMAP diet?
On a low FODMAP diet, you can typically enjoy about 1 cup (140 grams) of fresh pineapple per serving without triggering symptoms. Staying within this portion helps ensure you get the flavor and nutrients without overloading your gut with excess sugars that might cause discomfort.
What is the lowest FODMAP fruit?
Some of the lowest FODMAP fruits include strawberries, blueberries, grapes, and oranges, which are less likely to cause digestive distress in moderate amounts. These fruits offer bright, fresh flavors and antioxidants while being gentle on sensitive stomachs.
Is pineapple gut friendly?
Yes, pineapple is considered gut friendly when eaten in appropriate amounts. Its natural enzymes support digestion, and its low FODMAP status in moderate portions makes it a tasty, easy-to-digest fruit option that fits well into a gut-friendly diet like low FODMAP.
What food calms an IBS flare-up?
Foods that calm an IBS flare-up typically include gentle, low FODMAP options like cooked carrots, zucchini, white rice, and lean proteins such as chicken or fish. Bone broths, like those from Gourmend Foods, are also fantastic—they provide hydration, minerals, and soothing nutrients without irritating the gut.
How do I completely empty my bowels with IBS?
Completely emptying your bowels with IBS can be tricky since symptoms vary widely. Strategies that often help include staying well hydrated, eating soluble fiber found in oats and low FODMAP vegetables, and maintaining regular meal patterns. If constipation is an issue, gentle physical activity and working with your healthcare provider on tailored approaches are key.