Low FODMAP Ice Cream: The Ultimate IBS-Friendly Guide

Key Takeaways
- Low FODMAP ice cream can be enjoyed without triggering digestive distress for those managing IBS.
- Understanding ingredients and portion sizes is essential for choosing IBS-friendly ice cream.
- Smart ingredient swaps allow you to indulge in creamy desserts without discomfort.
- It is possible to enjoy gourmet ice cream while maintaining digestive peace.
Table of Contents
- Low FODMAP Ice Cream, What It Is and Why It Matters for Sensitive Digestion
- The Role of Lactose, Additives, and Sweeteners, Why Most Ice Creams Trigger IBS
- Comparing Low FODMAP Ice Cream Categories, Lactose-Free, Dairy-Free, and Sorbet
- Ingredient Labeling Mastery, How to Identify FODMAP Triggers in Ice Cream
- How to Make Homemade Low FODMAP Ice Cream, Simple, Gourmet Recipes
- Top Store-Bought Low FODMAP Ice Cream Brands & Flavors
- Creative Low FODMAP Ice Cream Toppings & Cones
- Addressing Common Ice Cream Problems, What to Do for Bloating, Texture, & Taste Issues
- FODMAPs, Ice Cream, and Nutritional Benefits, Balancing Enjoyment with Gut-Friendly Choices
- Final Thoughts & Flavorful Living, Empowering Enjoyment with Gourmend Foods
Low FODMAP Ice Cream: The Ultimate IBS-Friendly Guide
Finding low FODMAP ice cream that doesn't trigger digestive distress can feel impossible when you're managing IBS or gut sensitivity. The good news? You don't have to sacrifice creamy, indulgent desserts for digestive peace. With the right knowledge about ingredients, portions, and smart swaps, you can enjoy gourmet ice cream without the bloating, cramping, or discomfort that typically follows.
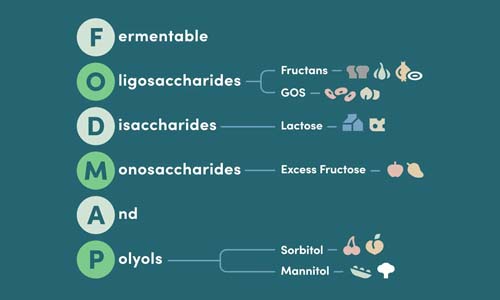
The key lies in understanding which specific carbohydrates, fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols, hide in traditional ice cream formulas and learning to navigate safer alternatives that deliver on both flavor and digestive comfort. For more inspiration on gut-friendly meals, explore our low FODMAP recipes.
The science is straightforward: FODMAPs are short-chain carbohydrates that draw water into your intestines and ferment rapidly, producing gas and triggering symptoms in sensitive individuals. When ice cream manufacturers remove or limit these compounds while maintaining rich texture and flavor, you get dessert that satisfies without the digestive aftermath.
Low FODMAP Ice Cream, What It Is and Why It Matters for Sensitive Digestion
Low FODMAP ice cream contains less than 1 gram of lactose per serving and avoids high-FODMAP ingredients like chicory root, excess fructose, and sugar alcohols that ferment in your gut. Unlike regular ice cream that can contain 4-8 grams of lactose per half-cup serving, these digestive-friendly versions use lactase-treated dairy, plant-based milks, or careful formulations that stay within safe thresholds.
Who Benefits Most from Low FODMAP Ice Cream?
- People with diagnosed IBS seeking symptom management
- Those with lactose intolerance looking beyond basic dairy-free options
- Anyone experiencing unexplained bloating after eating traditional ice cream
- Families wanting inclusive desserts that work for sensitive and non-sensitive digestive systems
The Role of Lactose, Additives, and Sweeteners, Why Most Ice Creams Trigger IBS

Traditional ice cream creates a perfect storm of FODMAP triggers. Lactose, the primary culprit, sits at 2-6 grams per typical scoop, well above the 1-gram safe threshold. But lactose isn't acting alone. Manufacturers often add chicory root (inulin) for fiber, whey protein concentrates with residual lactose, and sugar alcohols like sorbitol or mannitol that pass undigested into your colon.
Even dairy-free versions aren't automatically safe. Cashew-based ice creams contain galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS), while coconut milk varieties often include chicory root fiber or excess coconut cream that exceeds safe serving limits. Wheat-based stabilizers and honey sweeteners add additional FODMAP load that accumulates quickly in a single serving. For more on how rice fits into a low FODMAP diet, see is rice low FODMAP.
| Ingredient Category | Common FODMAP Triggers | Digestive Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Dairy Base | Lactose, whey protein | Osmotic effect, rapid fermentation |
| Sweeteners | Sorbitol, mannitol, honey | Gas production, cramping |
| Thickeners | Chicory root, wheat-based stabilizers | Bloating, altered gut bacteria |
| Flavor Additions | Cashew pieces, excess dried fruit | Cumulative FODMAP load |
Comparing Low FODMAP Ice Cream Categories, Lactose-Free, Dairy-Free, and Sorbet
Lactose-free ice cream uses lactase enzyme to break down milk sugar, maintaining traditional dairy richness while eliminating the primary FODMAP trigger. These options typically deliver the closest texture and mouthfeel to conventional ice cream, making them ideal for those who miss dairy-based desserts.
Dairy-free alternatives vary dramatically in FODMAP safety. Almond milk and rice milk bases generally stay within safe limits, while oat milk versions require portion control (limit to ⅓ cup) and coconut-based varieties need careful label reading for added fibers or excess coconut content.
Sorbet Analysis
- Naturally dairy-free and typically low FODMAP
- Clear ingredient lists with minimal additives
- Refreshing alternative with intense fruit flavors
- High fructose content in apple or pear varieties
- Added chicory root or inulin fibers
- Excess serving sizes that push sugar limits
Ingredient Labeling Mastery, How to Identify FODMAP Triggers in Ice Cream
Master the 5-second FODMAP scan by looking for these top 5 trigger ingredients in the first few lines: wheat (flour, thickeners), whey protein concentrate, high fructose corn syrup, chicory root extract, and sugar alcohols ending in "-ol" (sorbitol, mannitol, xylitol).
Quick FODMAP Label Scan
- Red flags: Any "-ol" sweeteners, chicory root, wheat-based ingredients
- Safe bets: Lactase enzyme, coconut milk, rice syrup, natural vanilla
- Portion matters: Even "safe" ingredients like almonds have FODMAP limits
The ingredient order reveals concentration, items listed first make up the largest portions. If you see high FODMAP ingredients in the top three positions, that product likely exceeds safe serving limits even in small portions. Conversely, trace amounts of borderline ingredients (like natural flavors containing small amounts of garlic extract) appearing at the end of long ingredient lists typically stay within acceptable ranges.
For ongoing ingredient guidance, Gourmend Foods' Recipe Conversion Tool helps identify safe substitutions when you're unsure about specific additives or want to adapt your favorite frozen dessert recipes for sensitive digestion.
How to Make Homemade Low FODMAP Ice Cream, Simple, Gourmet Recipes

Creating homemade low FODMAP ice cream gives you complete control over every ingredient, ensuring both exceptional flavor and digestive peace. The basic formula requires just three components: a low FODMAP milk base, natural sweetener, and your chosen flavor enhancer. For a savory meal idea, try this low FODMAP miso salmon recipe.
No-Churn Strawberry Almond Ice Cream delivers restaurant-quality results with minimal effort. Blend 2 cups unsweetened almond milk, ¼ cup pure maple syrup, and 1 cup fresh strawberries until smooth. Pour into a shallow container and freeze for 45 minutes, then whisk vigorously to break ice crystals. Repeat this process twice more at 45-minute intervals for creamy, scoopable texture.
Troubleshooting texture issues often comes down to timing and ratios. If your ice cream freezes too hard, increase the maple syrup slightly, natural sugars prevent excessive crystallization. For chalky or separated results, ensure your base mixture reaches room temperature before initial freezing, and maintain consistent whisking intervals during the freezing process.
The hands-on time rarely exceeds 15 minutes, while total preparation spans about 4 hours including freeze time. Each batch yields approximately 4 servings at ½ cup each, the perfect portion size for maintaining FODMAP safety while satisfying dessert cravings.
Top Store-Bought Low FODMAP Ice Cream Brands & Flavors
Navigate the freezer aisle confidently with these verified low FODMAP ice cream brands that prioritize both ingredient transparency and digestive comfort. Each recommendation includes specific flavor callouts and portion guidance based on FODMAP testing. For additional tips, see these low FODMAP ice cream tips from Monash University.
| Brand | Base | Best Flavors | Safe Serving | Availability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lactaid | Lactose-free dairy | Vanilla, Strawberry | ½ cup | Nationwide |
| So Delicious Coconut | Coconut milk | Vanilla Bean, Chocolate | ⅓ cup | Most grocers |
| Oat Dream | Oat milk | Vanilla, Mint Chip | ¼ cup | Health stores |
| Rice Dream | Rice milk | Vanilla, Carob | ½ cup | Specialty sections |
Serving size matters critically with store-bought options. Even FODMAP-friendly bases like coconut milk contain compounds that become problematic in larger portions. Stick to the recommended serving sizes above, and consider these your starting points, individual tolerance may require smaller portions initially.
Gourmend customers consistently report that Lactaid vanilla provides the closest taste and texture match to traditional dairy ice cream, while So Delicious coconut varieties offer the richest mouthfeel among plant-based options. Rice Dream works exceptionally well for those avoiding both dairy and nuts, though the lighter texture requires adjustment for dairy ice cream enthusiasts.
Creative Low FODMAP Ice Cream Toppings & Cones
Transform your low FODMAP ice cream into a gourmet experience with carefully portioned toppings that add texture and flavor without triggering digestive distress. The key lies in understanding both FODMAP limits and complementary flavor profiles.
Safe topping champions include chopped hazelnuts (limit 10 nuts), pure maple syrup, dairy-free dark chocolate chips, and fresh strawberry slices. These additions provide satisfying crunch, sweetness, and visual appeal while staying within established FODMAP thresholds. Cinnamon and vanilla extract can intensify flavor without adding FODMAPs. For cones, look for gluten-free, plain varieties made with rice or corn flour, and always check ingredient lists for hidden high-FODMAP additives.
Addressing Common Ice Cream Problems, What to Do for Bloating, Texture, & Taste Issues

Even with careful selection, ice cream challenges can arise. Here's how to troubleshoot the most common issues with low FODMAP ice cream consumption and preparation.
What to Do After Accidental High FODMAP Intake
- Hydrate immediately: Drink 16-20 oz of water to help flush excess FODMAPs
- Take a walk: Light movement aids digestion and reduces bloating
- Avoid doubling down: Skip other high FODMAP foods for 24-48 hours
- Consider enzyme support: Lactase supplements can help if lactose was the trigger
Texture Problems with Dairy-Free Options: Coconut and almond-based ice creams often freeze harder than dairy versions. Let them sit at room temperature for 5-7 minutes before scooping. Adding a tablespoon of neutral oil (like refined coconut oil) during homemade preparation creates smoother texture without affecting FODMAP content.
Taste Enhancement Without Risk: If your low FODMAP ice cream tastes bland, boost flavor with citrus zest (orange or lemon), pure vanilla extract, or a pinch of sea salt. These additions intensify existing flavors without introducing digestive triggers.
FODMAPs, Ice Cream, and Nutritional Benefits, Balancing Enjoyment with Gut-Friendly Choices
Understanding the nutritional landscape helps you make informed choices that support both pleasure and digestive health. For a comprehensive overview of IBS and its management, visit the NHS IBS resource.
| Ice Cream Type | Calcium (per ½ cup) | Protein | Added Sugars | Gut Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lactose-Free Dairy | 150-200mg | 4-6g | 12-16g | Minimal if truly lactose-free |
| Coconut Base | 40-60mg | 1-2g | 14-18g | Generally well-tolerated |
| Almond Base | 80-120mg | 2-3g | 10-14g | Safe in standard portions |
| Sorbet | 5-15mg | 0-1g | 20-25g | Depends on fruit and sweeteners |
Sugar Considerations: Even low FODMAP sweeteners can affect gut bacteria when consumed excessively. Limit ice cream portions to ½ cup servings, and balance indulgences with fiber-rich, low FODMAP foods like carrots, spinach, or quinoa in your other meals.
Nutrient Boosters: Add chopped hazelnuts (limit to 10 nuts), chia seeds (1 tablespoon), or unsweetened cocoa powder to increase protein, healthy fats, and minerals without compromising digestive comfort.
Final Thoughts & Flavorful Living, Empowering Enjoyment with Gourmend Foods
The journey to digestive comfort doesn't require sacrificing life's sweet pleasures. Low FODMAP ice cream options have evolved dramatically, offering genuine satisfaction without the aftermath of bloating or discomfort that once seemed inevitable.
Whether you choose carefully selected store brands, craft homemade versions, or explore creative toppings, the key lies in informed decision-making. Read labels with confidence, understand your personal tolerance levels, and remember that small portions of quality ingredients often deliver more satisfaction than larger servings of mediocre alternatives.
Success Story: Our Gourmend customer Sarah, who manages IBS, discovered that making her own almond milk ice cream with maple syrup and fresh mint gave her complete control over ingredients and portions. "I finally have dessert confidence again," she shared. "No more guessing games or digestive roulette."
At Gourmend Foods, we understand that food should nourish both body and spirit. While our expertise centers on broths and seasonings, the principles remain constant: clean ingredients, scientific backing, and flavor that never compromises. Your ice cream choices deserve the same thoughtful approach.
Explore our complete collection of low FODMAP recipes for more inspiration, and use our recipe conversion tool to adapt your favorite frozen dessert recipes safely. Digestive wellness and culinary joy aren't mutually exclusive, they're perfectly complementary when you have the right knowledge and tools.
Frequently Asked Questions
What ingredients should I look for or avoid when choosing low FODMAP ice cream to prevent IBS symptoms?
Look for ice creams with less than 1 gram of lactose per serving and avoid high-FODMAP ingredients like chicory root, excess fructose, and sugar alcohols. Choose options with simple, clean ingredients and steer clear of additives that ferment in the gut to keep digestion comfortable.
How do lactose-free and dairy-free ice creams differ in their impact on digestive health for people with IBS?
Lactose-free ice creams use dairy treated to break down lactose, making them easier to digest for many with IBS, while dairy-free options rely on plant-based milks that naturally contain no lactose. Both can be gut-friendly, but individual tolerance varies, so choosing based on ingredient transparency and personal response is key.
Can homemade low FODMAP ice cream match the taste and texture of store-bought options while being gut-friendly?
Absolutely. With smart ingredient swaps like lactose-free milk or plant-based alternatives and simple recipes, homemade low FODMAP ice cream can deliver creamy, gourmet flavor without digestive discomfort. Plus, making it yourself lets you control every ingredient for maximum gut-friendliness.
What portion sizes of low FODMAP ice cream are recommended to minimize digestive discomfort?
Keeping servings under half a cup helps prevent IBS symptoms by limiting exposure to fermentable carbohydrates. Enjoying smaller portions allows you to indulge in creamy desserts while maintaining digestive ease and comfort.