Is Cream Cheese Low FODMAP? Science + Flavor Tips

Key Takeaways
- Cream cheese can be enjoyed on a low FODMAP diet with proper portion control.
- The answer to whether cream cheese is low FODMAP depends on serving size and product choice.
- Understanding the science behind FODMAP content helps maintain digestive comfort.
- Gourmend Foods promotes enjoying flavorful foods without strict restrictions.
Table of Contents
- What Makes a Cheese Low FODMAP? Science, Lactose & Serving Size
- Is Cream Cheese Low FODMAP? Facts, Data, and Everyday Practicality
- Cream Cheese vs. Other Cheeses: How Does It Compare on the Low FODMAP Scale?
- How to Choose Cream Cheese That's Truly Low FODMAP: A Practical Shopper's Guide
- Best Ways to Enjoy Cream Cheese on a Low FODMAP Diet: Tips, Swaps & Flavor-First Recipes
Is Cream Cheese Low FODMAP? The Definitive Answer for IBS & Gourmet Cooking
For anyone wondering is cream cheese low FODMAP, the answer isn't a simple yes or no, it's about smart portioning and strategic choices. At Gourmend Foods, we believe in abundance, not restriction. You can absolutely enjoy cream cheese's rich, tangy flavor while maintaining digestive comfort, but the key lies in understanding the science behind serving sizes and selecting the right products.
The low FODMAP question matters because cream cheese appears in countless gourmet applications, from herb-infused spreads to creamy pasta sauces. Rather than eliminating this versatile ingredient entirely, we'll show you how to make it work within your dietary needs without sacrificing the bold flavors you crave. If you're looking for more low FODMAP meal inspiration, try this recipe for low FODMAP miso salmon for a delicious and gut-friendly dinner option.
Here's the crucial insight: "low FODMAP" doesn't mean eliminating all dairy. Most dairy-related digestive issues stem from lactose, a specific type of FODMAP sugar. This means you can strategically include certain dairy products, including cream cheese, without abandoning your favorite flavors. For another creative side, check out these low FODMAP crisp roasted baby potatoes that pair perfectly with creamy spreads.
What Makes a Cheese Low FODMAP? Science, Lactose & Serving Size
FODMAPs in Plain English, Why They Matter for Your Gut
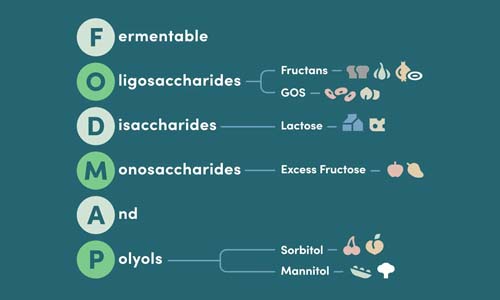
FODMAPs are fermentable carbohydrates that can trigger digestive symptoms like bloating, gas, and abdominal discomfort in people with IBS. The acronym stands for Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols, but what matters most is understanding that these compounds draw water into your intestines and ferment rapidly, creating the uncomfortable symptoms many experience.
Here's the crucial insight: "low FODMAP" doesn't mean eliminating all dairy. Most dairy-related digestive issues stem from lactose, a specific type of FODMAP sugar. This means you can strategically include certain dairy products, including cream cheese, without abandoning your favorite flavors.
Lactose: The Dairy Sugar to Watch
Cream cheese contains more lactose than aged cheeses because of how it's produced. While hard cheeses like cheddar lose most lactose during aging (containing less than 0.1g per serving), cream cheese retains 2-3g per standard serving due to its fresh, unaged nature and higher moisture content.
This lactose difference explains why someone might tolerate aged parmesan freely but experience symptoms from larger portions of cream cheese. The manufacturing process matters, aged cheeses naturally break down lactose over time, while fresh cheeses like cream cheese preserve more of the original milk sugars.
Why Serving Size Rules Everything
FODMAP tolerance operates on a threshold system, your digestive system can handle small amounts of these compounds, but symptoms appear when you exceed your personal limit. For cream cheese low FODMAP guidelines, this threshold sits around 40g (2 tablespoons) for most people.
Real-world application: spreading 1-2 tablespoons of cream cheese on gluten-free toast with chive sprigs delivers rich, satisfying flavor without triggering digestive distress. Exceed this amount, and the lactose load crosses into symptom-producing territory. This isn't about deprivation, it's about strategic enjoyment that respects your body's limits.
Is Cream Cheese Low FODMAP? Facts, Data, and Everyday Practicality

Monash University & Leading Research: The Line in the Sand
Monash University, the gold standard for FODMAP research, rates regular cream cheese as low FODMAP up to 2 tablespoons (40g). Their testing shows that within this portion, the lactose content remains below the threshold that typically triggers symptoms in sensitive individuals. For more information on FODMAPs and IBS, you can visit Monash University's FAQ page.
Beyond 2 tablespoons, the FODMAP load rises significantly. At 3-4 tablespoons, most people following a low FODMAP diet will experience symptoms. This research provides the scientific foundation for confident portion control, you're not guessing, you're following evidence-based guidelines.
Breaking Down Brands & Labels: Navigating the Aisle
Not all cream cheeses are created equal. Some brands add milk solids, whey, or sweeteners that increase lactose content beyond the standard range. When evaluating whether cream cheese is low FODMAP, look for options with minimal ingredients. The ideal label reads simply: cream, milk, salt, and stabilizers like locust bean gum. Avoid products listing inulin, chicory root, or artificial sweeteners, these can trigger symptoms even in small amounts.
Here's your shopping checklist: sugar content under 1g per 2-tablespoon serving, ingredient lists with fewer than six items, and lactose content clearly disclosed. Some mainstream brands meet these criteria without official certification, making them practical choices for everyday cooking.
Lactose-Free Cream Cheese: Your Safest Bet for Digestive Peace
Lactose-free cream cheese removes the guesswork entirely. The lactase enzyme breaks down lactose during production, creating a product that's naturally gentler on sensitive digestive systems. Most lactose-free varieties contain less than 0.1g lactose per serving, well below the threshold that triggers symptoms.
This option works especially well if you're extra-sensitive or new to the low FODMAP approach. You can confidently use the full 2-tablespoon serving without worry, making recipe planning significantly easier. Store-brand lactose-free versions deliver the same creamy texture and tangy flavor as traditional cream cheese.
Cream Cheese vs. Other Cheeses: How Does It Compare on the Low FODMAP Scale?
Cream Cheese vs. Hard Cheeses: Why Age Matters for Your Gut
Hard, aged cheeses like cheddar, parmesan, and Swiss contain virtually no lactose, typically less than 0.1g per serving. The aging process naturally breaks down lactose, making these cheeses freely enjoyable for most people following a low FODMAP diet. Cream cheese, by contrast, contains 2-3g lactose per 2-tablespoon serving because it's fresh and unaged.
However, cream cheese offers unique culinary advantages that aged cheeses can't match. Its smooth, spreadable texture and mild tang make it irreplaceable in bagel spreads, creamy dips, and dessert applications. When is cream cheese low FODMAP becomes your question, remember that portion control unlocks its potential where aged cheeses might be too sharp or crumbly for your intended use.
| Cheese Type | Lactose Content (per serving) | Low FODMAP Serving Size | Best Culinary Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cream Cheese | 2-3g | 2 tablespoons (40g) | Spreads, dips, desserts |
| Cheddar (aged) | <0.1g | Unlimited | Melting, snacking |
| Parmesan | <0.1g | Unlimited | Grating, flavor enhancement |
| Mozzarella | 0.1-0.5g | 1 cup shredded | Pizza, melting dishes |
Cream Cheese vs. Ricotta and Cottage Cheese: Fresh Cheese Face-Off
Among fresh cheeses, cream cheese offers moderate FODMAP levels compared to ricotta and cottage cheese. Ricotta contains similar lactose levels (2-4g per ½ cup) but allows larger serving sizes, up to ½ cup is considered low FODMAP. Cottage cheese sits in the middle, with ⅓ cup as the recommended limit.
For recipe substitutions, ricotta works beautifully in lasagna and stuffed shells where you need volume, while cream cheese excels in applications requiring smoothness and richness. The texture difference is significant: ricotta's grainy consistency versus cream cheese's silky uniformity makes each irreplaceable in specific dishes. When determining low FODMAP cream cheese alternatives, consider your recipe's texture requirements alongside FODMAP content.
Plant-Based Alternatives: Navigating Vegan Cream Cheese Options
Vegan cream cheese alternatives can be excellent low FODMAP choices, but ingredient scrutiny is essential. Coconut-based versions typically contain minimal FODMAPs, while cashew-based options work well in 2-tablespoon servings. However, many commercial vegan cream cheeses contain hidden FODMAP triggers like inulin, chicory root, or apple fiber as texture enhancers.
Some almond- and cashew-based brands offer cleaner ingredient profiles, though they're not officially certified low FODMAP. Always check labels for sneaky additions like onion powder or high-FODMAP thickeners. These alternatives often provide similar spreadability and tang, making them viable substitutes when dairy isn't an option. For more on plant-based low FODMAP meals, you might enjoy this recipe for low FODMAP mushroom risotto.
How to Choose Cream Cheese That's Truly Low FODMAP: A Practical Shopper's Guide
Reading Labels Like a Pro: Spotting Hidden FODMAP Triggers
When reading cream cheese labels, always check for added ingredients that could increase FODMAP content, such as inulin, chicory root, or high-lactose milk solids. For a deeper dive into the science behind FODMAPs and their impact on digestive health, see this peer-reviewed article on FODMAPs and IBS.
Best Ways to Enjoy Cream Cheese on a Low FODMAP Diet: Tips, Swaps & Flavor-First Recipes

Easy, Gourmet-Ready Low FODMAP Uses for Cream Cheese
Transform simple ingredients into sophisticated snacks with strategic cream cheese applications. Whip 2 tablespoons with fresh chive sprigs and spread on gluten-free crackers for an elegant appetizer. Stuff mini bell peppers with the mixture for colorful party bites, or dollop onto low FODMAP pizza made with rice flour crust.
Sweet applications shine equally bright. Spread cream cheese on toasted gluten-free bagels topped with fresh strawberry slices, or swirl into morning oats with blueberries for protein-rich breakfast bowls. Each application respects the 2-tablespoon limit while delivering maximum flavor impact through thoughtful ingredient pairing. For a comforting main dish, try this low FODMAP braised short ribs recipe.
Quick Gourmet Swaps if You Can't Tolerate Cream Cheese
Lactose-free cream cheese provides the most seamless substitution, maintaining identical texture and flavor profiles. For completely dairy-free options, coconut cream (the thick layer from chilled coconut milk) works beautifully in sweet applications, while cashew-based spreads handle savory uses effectively.
| Original Use | Best Substitute | Flavor Notes | FODMAP Safety |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bagel spread | Lactose-free cream cheese | Identical to original | Safe up to 2 tbsp |
| Sweet dips | Coconut cream | Subtle tropical notes | Safe up to ¼ cup |
| Savory spreads | Cashew-based cheese | Nutty, creamy | Check ingredients carefully |
How Gourmend Makes Cream Cheese Work: Chef's Kitchen Secrets
We elevate cream cheese low FODMAP dishes by building layers of flavor without problematic ingredients. Fresh chive sprigs and green leek tops provide the savory depth traditionally supplied by garlic bulbs and onion, while scallion greens add subtle bite to cream cheese-based dips and spreads.
Our secret weapon combines cream cheese with Gourmend shelf-stable broth carton for incredibly rich, creamy sauces that stretch your 2-tablespoon allowance further. Mix equal parts cream cheese and our chicken broth for pasta sauces, or blend with vegetable broth and fresh herbs for sophisticated vegetable dips. This technique delivers restaurant-quality results while respecting your digestive comfort. For more inspiration, explore our Low FODMAP Recipes or try our Low FODMAP Recipe Conversion Tool to adapt your favorites.
Frequently Asked Questions
What factors determine whether cream cheese is considered low FODMAP?
Cream cheese is considered low FODMAP based primarily on its lactose content and serving size. Choosing products with lower lactose and keeping portions moderate helps maintain digestive comfort while enjoying its creamy texture.
How does the lactose content in cream cheese compare to other types of cheese on a low FODMAP diet?
Cream cheese generally contains more lactose than aged cheeses like cheddar or Parmesan, which have very low lactose levels. However, it has less lactose than fresh cheeses such as ricotta, making portion control key to fitting cream cheese into a low FODMAP diet.
What is the recommended serving size of cream cheese to avoid triggering IBS symptoms?
A serving size of up to 40 grams of cream cheese is typically considered low FODMAP and less likely to cause digestive discomfort. Staying within this portion helps you enjoy cream cheese without overloading on lactose.
How can I incorporate cream cheese into my meals while following a low FODMAP diet?
You can add cream cheese in small amounts to dishes like herb spreads, sauces, or dips to boost flavor and creaminess. Pair it with low FODMAP ingredients and use Gourmend broths or seasonings to create balanced, gut-friendly meals that don’t sacrifice gourmet taste.