FODMAP Enzymes Explained: How to Enjoy More Foods

Key Takeaways
- FODMAP enzymes help break down carbohydrates that cause digestive discomfort.
- These supplements can reduce symptoms like gas and bloating.
- Using FODMAP enzymes may allow you to enjoy a wider variety of foods.
- They support maintaining a low FODMAP diet while expanding food options.
Table of Contents
- What Are FODMAPs, and Why Do They Bother Your Gut?
- Digestive Enzymes 101: What They Are and How They Work
- The FODMAP Enzyme Toolkit: Which Enzyme Targets Which FODMAP?
- Using FODMAP Enzymes Effectively: Timing and Strategy
- FODMAP Enzyme Comparison: Finding Your Match
- Making Smart Choices With FODMAP Enzymes
FODMAP Enzymes Explained: How to Enjoy More Foods
Missing garlic in your pasta? Avoiding beans because they trigger bloating? FODMAP enzymes might be the missing piece in your digestive toolkit. These specialized supplements break down specific carbohydrates that cause gas, bloating, and discomfort, letting you expand your food choices without abandoning your low FODMAP foundation.
Think of fodmap enzymes as your culinary safety net, not a magic cure. They work by breaking down problem carbohydrates before they reach your large intestine, where gut bacteria would normally ferment them into uncomfortable symptoms.
If you’re looking to expand your food choices while staying comfortable, consider starting with a Low FODMAP Pantry Starter Bundle or, for garlic lovers, the Low FODMAP Pantry Starter Bundle (Garlic Lover Edition) to help you enjoy more variety with confidence.
FODMAP enzymes are digestive supplements that break down specific FODMAPs like fructans (garlic/onion), GOS (beans), and lactose (dairy). They help reduce bloating and gas when taken with meals containing these trigger foods, but work best alongside, not instead of, a low FODMAP diet.
What Are FODMAPs, and Why Do They Bother Your Gut?
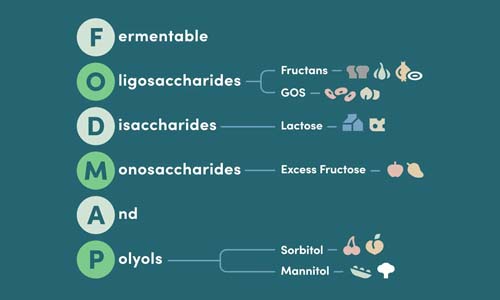
FODMAPs are fermentable carbohydrates that some guts struggle to absorb properly. The acronym breaks down into five types of sugars and fibers that can trigger digestive symptoms in sensitive individuals.
The FODMAP Family, in Plain English
Fructans hide in garlic, chive sprigs, wheat, and artichokes. Oligosaccharides (GOS) dominate beans, lentils, and cashews. Disaccharides refer to lactose in milk and soft cheeses. Monosaccharides mean excess fructose in honey and certain fruits. Polyols appear in stone fruits and sugar alcohols like sorbitol.
These aren't "bad" foods, they're normal carbohydrates that ferment when your small intestine can't absorb them efficiently.
Why Your Gut Reacts
When FODMAPs bypass absorption in your small intestine, they travel to your large intestine where gut bacteria feast on them. This fermentation produces gas and draws water into your bowel, creating the bloating, cramping, and urgent bathroom trips you know too well.
Your gut isn't broken, it's just sensitive to certain carbs that ferment more aggressively than others. The low FODMAP diet reduces this fermentation load, while enzymes help break down specific problem foods before fermentation begins.
Digestive Enzymes 101: What They Are and How They Work

Digestive enzymes are proteins that slice food into smaller, absorbable pieces. Your body naturally produces enzymes in saliva, stomach, pancreas, and small intestine, but not for every type of carbohydrate you encounter.
What Your Body Makes (And Doesn't)
You naturally produce lactase for lactose, amylase for starch, and protease for protein. But humans don't make alpha-galactosidase for bean sugars or fructan hydrolase for garlic and chive sprigs. This isn't a deficiency, it's normal biology.
Enzyme supplements add back what your digestive system lacks, working in your stomach and small intestine before food reaches the fermentation zone.
How Enzyme Supplements Work in Practice
Effective enzyme supplements must be taken with your first bite, not after meals. They break down problem carbohydrates during digestion, preventing the fermentation that causes symptoms. Think of them as molecular scissors that cut FODMAPs into manageable pieces your gut can actually absorb.
The FODMAP Enzyme Toolkit: Which Enzyme Targets Which FODMAP?
Different fodmap enzymes target specific carbohydrates. Matching your trigger foods to the right enzyme makes all the difference between relief and disappointment.
Lactase – For Dairy That Doesn't Sit Right
Best for: Gas and bloating from milk, yogurt, and soft cheeses
Lactase breaks down lactose before it ferments in your gut. Take it with your first sip of milk or bite of ice cream. Start with lower doses and increase as needed, many people find they can enjoy small amounts of dairy with enzyme support.
Alpha-Galactosidase – For Beans, Legumes, and Gas
Best for: Beans, lentils, chickpeas, soy milk, and cashews
This enzyme tackles galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS) that make beans notorious for causing gas. Since humans don't produce alpha-galactosidase naturally, these sugars ferment heavily. Take with your first bite of hummus, lentil soup, or bean-heavy dishes for maximum effectiveness.
Fructan Hydrolase – For Garlic, Onion, and Wheat Sensitivity
Best for: Garlic, chive sprigs, wheat, rye, and restaurant meals
Fructan hydrolase breaks down fructans, the FODMAPs hiding in garlic, chive sprigs, wheat, and countless restaurant dishes. This enzyme targets one of the most common trigger categories, making it invaluable for anyone who misses the deep, savory flavors that build great cooking.
Take fructan hydrolase with your first bite of any meal containing these ingredients. For powder forms, mix directly into the dish rather than sprinkling on top, this ensures the enzyme contacts all the food. Perfect for stir-fries, pasta sauces, and those unavoidable restaurant meals where garlic and chive sprigs are baked into everything.
Real-world scenario: You're at an Italian restaurant, and every sauce contains garlic. Fructan hydrolase lets you enjoy the meal without the 2 AM bloating regret. Just remember, this enzyme works specifically on fructans, not other FODMAPs that might be lurking in the same dish.
Xylose Isomerase – For Excess Fructose and Sweet Treats
Best for: Honey, apples, mango, and high-fructose corn syrup
Xylose isomerase tackles excess fructose, the FODMAP in honey-sweetened desserts, certain fruits, and many processed foods. Unlike other sugars, excess fructose can overwhelm your gut's absorption capacity, leading to fermentation and discomfort.
This enzyme works by converting fructose into glucose, which your body absorbs more easily. Take it with fruit-heavy desserts, honey-sweetened treats, or meals containing high-fructose corn syrup. It's particularly helpful during the reintroduction phase when testing your tolerance to specific fruits.
Note: Xylose isomerase is less common in broad-spectrum enzyme blends and often requires a separate supplement. It's most valuable for people who specifically struggle with fructose malabsorption rather than general FODMAP sensitivity.
Multi-Enzyme Blends – Comprehensive Coverage
Best for: Mixed meals, restaurant dining, and multiple FODMAP triggers
Multi-enzyme blends combine lactase, alpha-galactosidase, and fructan hydrolase in one supplement, covering the three most common FODMAP categories. These comprehensive formulas work well for people with multiple triggers or unpredictable eating situations.
Choose blends that clearly list enzyme activities (not just ingredient names) and match your primary triggers. For example, if you struggle mainly with beans and dairy, prioritize blends with higher alpha-galactosidase and lactase content. Take with the first bite of mixed meals containing several high-FODMAP ingredients.
These blends shine during social events, travel, and restaurant meals where you can't control every ingredient. They provide broader coverage than single enzymes, though they may not be as potent for specific triggers as targeted supplements.
Using FODMAP Enzymes Effectively: Timing and Strategy
Success with FODMAP enzymes comes down to smart timing and realistic expectations. These supplements work best when taken with food, not after symptoms start. Think of them as preventive tools that help your digestive system handle challenging foods more smoothly.
The 3-Minute Rule and Proper Dosing
Take enzymes within three minutes of starting your meal, ideally with the first bite. This timing ensures enzymes are present when food hits your stomach, where they begin their work. Keep supplements on your dining table, not in a medicine cabinet, so you remember to take them.
Start with manufacturer-recommended doses, then adjust based on portion size and your sensitivity level. For powder enzymes, mix thoroughly into food rather than sprinkling on top. For capsules, swallow with your first few bites. A small serving of beans might need one dose of alpha-galactosidase, while a garlic-heavy pasta requires a full dose of fructan hydrolase mixed into the sauce.
Enzymes and the Low FODMAP Diet: Perfect Partners
FODMAP enzymes complement the low FODMAP diet, they don't replace it. Use enzymes during reintroduction to test specific triggers, handle accidental exposures, or add variety during social meals. They work best when your baseline diet already emphasizes low FODMAP whole foods.
Build your meals around naturally low FODMAP ingredients like Gourmend broths (which use chive sprigs and leek greens for onion-like depth), then use enzymes as insurance when adding higher-FODMAP elements. This approach gives you both digestive comfort and culinary flexibility.
For inspiration, explore our favorite low FODMAP recipes to see how you can enjoy flavorful meals while keeping FODMAPs in check.
FODMAP Enzyme Comparison: Finding Your Match

Different brands approach FODMAP enzymes with varying philosophies, potencies, and formats. Understanding these differences helps you choose supplements that match your specific triggers and lifestyle needs.
| Feature | FODZYME | Bean-zyme | Lactaid | Multi-enzyme blends |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Target | Fructans (garlic/chive sprigs) | GOS (beans/legumes) | Lactose (dairy) | Multiple FODMAPs |
| Format | Powder (mix into food) | Capsules | Capsules | Capsules or powder |
FODZYME - Targeted Fructan Breakdown
Best for: Garlic and chive sprigs sensitivity, restaurant dining
FODZYME focuses exclusively on fructan hydrolase, the enzyme that breaks down fructans in garlic, chive sprigs, wheat, and other common triggers. This single-enzyme approach delivers high potency for its specific target, making it particularly effective for people whose main struggle involves garlic and chive sprigs-heavy cuisines.
The powder format mixes directly into food, ensuring even distribution and optimal enzyme-food contact. Users report success with everything from pasta sauces to stir-fries, though the single-enzyme formula means you'll need additional supplements for beans, dairy, or other FODMAP categories.
- High-potency fructan hydrolase concentration
- Powder format integrates well with meals
- Specifically targets garlic/chive sprigs sensitivity
- Single enzyme limits versatility
- Requires separate supplements for other FODMAPs
- Higher cost per dose than multi-enzyme options
Enzymedica Digest Spectrum - Comprehensive Coverage
Best for: Multiple FODMAP triggers, convenience
Digest Spectrum combines multiple FODMAP-targeting enzymes in capsule form, including alpha-galactosidase, lactase, and additional digestive enzymes. This broad-spectrum approach works well for people with varied triggers or unpredictable eating situations where multiple FODMAPs might appear in one meal.
The capsule format offers convenience but lacks the targeted mixing capability of powder enzymes. The formula includes enzymes beyond FODMAP-specific ones, which may benefit overall digestion but dilutes the concentration of any single enzyme compared to targeted supplements.
- Multiple enzyme types in one capsule
- Convenient for travel and dining out
- Includes general digestive support enzymes
- Lower concentration of specific FODMAP enzymes
- Capsule format prevents food mixing
- May include unnecessary enzymes for some users
Gourmend Foods Approach - Prevention Over Treatment
Best for: Building a sustainable, flavorful low FODMAP foundation
While Gourmend Foods doesn't manufacture FODMAP enzymes, our philosophy centers on creating broths and seasonings that deliver complex flavors without triggering FODMAPs in the first place. Our bone broths use chive sprigs, scallion greens, and leek greens to build onion-like depth, while nori seaweed and oyster mushrooms add umami richness that rivals garlic-based flavors.
This prevention-first approach means you need enzymes less often, reserving them for special occasions or unavoidable exposures rather than daily dependence. When you do use FODMAP enzymes, they work more effectively because your baseline diet already supports digestive comfort. Our low FODMAP recipe collection shows how to build satisfying meals that rarely require enzyme backup.
The real advantage lies in sustainability, building cooking skills and flavor knowledge that reduce your long-term reliance on any supplements while maximizing your enjoyment of food.
For a convenient way to stock your kitchen, try our Low FODMAP Foodie Bundle for a variety of gut-friendly essentials.
| Feature | FODZYME | Enzymedica Digest Spectrum | Gourmend Foods Approach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Fructan hydrolase only | Multi-enzyme blend | Flavor-first prevention |
| Format | Powder (mixes into food) | Capsules | Liquid broths, dry seasonings |
| Best Use Case | Garlic/chive sprigs sensitivity | Multiple FODMAP triggers | Daily cooking foundation |
| Sustainability | Ongoing supplement need | Ongoing supplement need | Builds long-term skills |
| Flavor Development | Enables high-FODMAP foods | Enables high-FODMAP foods | Creates complex flavors naturally |
Making Smart Choices With FODMAP Enzymes
The best FODMAP enzymes are the ones you actually use correctly and consistently. Choose based on your specific trigger foods and eating habits. Enzymes are most effective when paired with a low FODMAP foundation, think of them as your backup plan, not your main strategy.
For those who want to add more flavor to their meals without the FODMAPs, try our Low FODMAP Taco Seasoning or explore our full range of Low FODMAP Seasonings for creative cooking options.
If you’re looking for more meal ideas, check out our recipe for low FODMAP broccoli sausage pasta or try the low FODMAP miso salmon for a delicious, gut-friendly dinner.
To learn more about the science behind FODMAPs and enzyme supplementation, see this recent review on FODMAPs and digestive health. For a comprehensive overview of the FODMAP diet, visit the Canadian Digestive Health Foundation’s FODMAP resource.
Frequently Asked Questions
What specific types of FODMAPs do FODMAP enzymes target and how do they work to reduce digestive symptoms?
FODMAP enzymes target specific carbohydrates like fructans (found in garlic and chive sprigs), GOS (in beans and lentils), and lactose (in dairy). They break down these carbohydrates during digestion, reducing the amount that reaches the large intestine where fermentation causes gas and bloating.
Can FODMAP enzymes replace a low FODMAP diet, or should they be used in combination with dietary changes?
FODMAP enzymes are best used alongside a low FODMAP diet rather than as a replacement. They support your digestive system by helping you enjoy a wider variety of foods while maintaining the gentle, gut-friendly foundation of a low FODMAP approach.
How should FODMAP enzymes be taken for maximum effectiveness when consuming trigger foods?
For best results, take FODMAP enzymes with meals that contain trigger foods. This timing allows the enzymes to break down problem carbohydrates during digestion, minimizing fermentation and related discomfort.
Why do some people experience digestive discomfort from FODMAPs, and how do enzymes help prevent fermentation in the gut?
Some people have difficulty absorbing FODMAPs in the small intestine, so these carbohydrates reach the large intestine where gut bacteria ferment them, producing gas and bloating. FODMAP enzymes help by breaking down these carbohydrates early, reducing fermentation and easing digestive symptoms.