Are Black Beans Low FODMAP? Evidence-Based Guide

Key Takeaways
- FODMAPs are short-chain carbohydrates that are poorly digested in the small intestine.
- These compounds reach the colon where gut bacteria ferment them rapidly.
- The fermentation process produces gas and draws water into the intestines.
- People with IBS or sensitive digestion may experience bloating, cramping, and discomfort from FODMAPs.
Table of Contents
- What Are FODMAPs and Why Do They Matter for Black Beans?
- Nutritional Profile and Health Benefits of Black Beans
- Are Black Beans Low FODMAP? Serving Sizes and Scientific Evidence
- Comparing Black Beans to Other Beans: FODMAP Content & Digestive Friendliness
- Preparation and Cooking Techniques: Safely Including Black Beans in Low FODMAP Recipes
- Black Bean Products on Store Shelves: Ingredient Label Reading for FODMAP Safety
- Decoding Black Bean Paste, Sauce, and Fermented Beans: FODMAP Content & Culinary Use
- Troubleshooting, What If Black Beans Cause IBS Symptoms? Solutions and Alternatives
- Final Recommendations for the Flavor-First, Low FODMAP Black Bean Experience
What Are FODMAPs and Why Do They Matter for Black Beans?
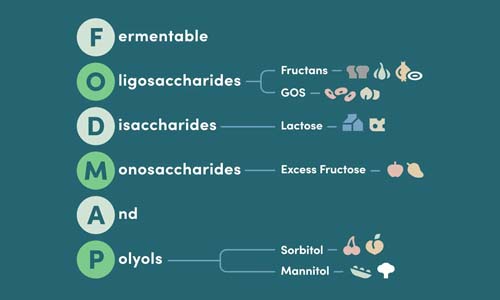
FODMAPs, Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols, are short-chain carbohydrates that resist digestion in the small intestine. When these compounds reach your colon, gut bacteria ferment them rapidly, producing gas and drawing water into the intestines. For those with IBS or sensitive digestion, this fermentation triggers bloating, cramping, and digestive discomfort.
Black beans contain galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS), a specific type of oligosaccharide that makes them particularly challenging for sensitive guts. However, here's the crucial insight: are black beans low FODMAP? Yes, but only in controlled portions. Monash University research shows canned black beans remain low FODMAP at servings up to ¼ cup, but cross into high-FODMAP territory beyond that threshold.
Nutritional Profile and Health Benefits of Black Beans

Even in gut-friendly portions, black beans deliver impressive nutritional density. A 2-tablespoon serving (40g) provides approximately 60 calories, 4 grams of plant protein, 5 grams of fiber, and significant amounts of folate, magnesium, and iron. These small but mighty legumes also contain anthocyanins, the same antioxidants that give blueberries their superfood status.
For those following a low FODMAP approach, this nutrient concentration becomes particularly valuable. You're maximizing nutritional impact within digestive comfort zones, supporting heart health and stable blood sugar without the bloating that larger bean servings might cause. The fiber content, while modest in small portions, still contributes to digestive wellness when part of a varied, gut-friendly diet.
The protein quality in black beans complements other low FODMAP foods beautifully. Pair your 2-tablespoon serving with quinoa, rice, or our Gourmend shelf-stable broth carton to create complete amino acid profiles that satisfy both nutritional needs and flavor expectations. This approach transforms restriction into abundance, you're not limiting beans, you're optimizing them.
Are Black Beans Low FODMAP? Serving Sizes and Scientific Evidence
Monash University's comprehensive FODMAP testing reveals precise thresholds for black bean consumption. Canned black beans test low FODMAP at 2 tablespoons (40g), moderate at ¼ cup (60g), and high FODMAP beyond ½ cup. This serving-size dependency explains why some people tolerate small amounts while experiencing symptoms with larger portions.
| Preparation Method | Low FODMAP Serving | FODMAP Level | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Canned, drained & rinsed | 2 tablespoons (40g) | Low | Safest option |
| Boiled from dried | 2 tablespoons (40g) | Low-Moderate | Higher FODMAP than canned |
| Black bean paste | 1 tablespoon (20g) | Moderate | Often contains garlic/onion |
| Fermented black beans | 1 teaspoon (5g) | Low | Intense flavor, use sparingly |
The canning process reduces FODMAP content by allowing some oligosaccharides to leach into the liquid, which you discard when draining. This explains why canned black beans consistently test lower in FODMAPs than home-cooked dried beans. For optimal digestive comfort, always drain and rinse canned beans thoroughly before use.
When planning meals, consider that fodmap black beans work best as flavor accents rather than primary protein sources. Two tablespoons per person in tacos, salads, or soups provides satisfying taste and nutrition while respecting digestive boundaries.
Comparing Black Beans to Other Beans: FODMAP Content & Digestive Friendliness
Not all beans behave equally in the FODMAP landscape. Understanding these differences helps you choose the most gut-friendly options for various recipes and flavor profiles.
Chickpeas (Canned, Rinsed) - Most Generous Serving
Best for: Mediterranean dishes, hummus alternatives, hearty salads
Canned chickpeas offer the largest low FODMAP serving at ¼ cup (60g), making them ideal for larger portions in salads, stews, and Mediterranean-inspired dishes. Their creamy texture and mild flavor pair beautifully with chive sprigs and green leek tops for onion-like depth without digestive distress.
Pros:
- Largest safe serving size among legumes
- Versatile protein for multiple cuisines
- Excellent fiber-to-FODMAP ratio
Considerations:
- Higher calorie density than other options
- May cause bloating if portion exceeded
Green Lentils (Canned, Rinsed) - Quick-Cooking Protein
Best for: Weeknight dinners, grain bowls, soup bases
Green lentils match chickpeas with a ¼ cup safe serving but cook faster and hold their shape better in recipes. They're particularly excellent when simmered in Gourmend shelf-stable broth carton for added umami depth.
Edamame (Frozen, Shelled) - Highest Volume Option
Best for: Snacking, Asian-inspired dishes, salad protein
With a generous ½ cup (75g) serving size, edamame offers the most volume for FODMAP-sensitive eaters. These young soybeans provide complete protein and work exceptionally well in stir-fries enhanced with garlic-chive stems.
Black Beans (Canned, Rinsed) - Concentrated Flavor Impact
Best for: Latin cuisine, flavor-forward dishes, color contrast
Though limited to 2 tablespoons (40g), black beans deliver intense, earthy flavor that transforms small portions into satisfying meals. Their deep color and robust taste make them ideal for dishes where a little goes a long way.
Preparation and Cooking Techniques: Safely Including Black Beans in Low FODMAP Recipes

The key to enjoying black beans while maintaining digestive comfort lies in proper preparation techniques that naturally reduce FODMAP content. Canned black beans, when properly rinsed, offer the most reliable low FODMAP option for home cooks.
Essential Preparation Steps:
- Choose canned over dried: The canning process naturally reduces oligosaccharide levels
- Rinse thoroughly: Drain and rinse canned beans for 30 seconds under cold water to remove excess starches
- Measure precisely: Use a measuring spoon, not estimation, to maintain the 2-tablespoon serving limit
For maximum flavor impact within FODMAP limits, build depth using chive sprigs, green leek tops, and garlic-chive stems instead of traditional aromatics. Simmering your measured black beans in Gourmend shelf-stable broth carton adds restaurant-quality umami without compromising digestive safety.
When incorporating black beans into recipes, distribute the 2-tablespoon serving across multiple components, add half to your base sauce and half as garnish. This technique maximizes visual appeal and flavor distribution while respecting FODMAP thresholds that keep your gut comfortable.
Black Bean Products on Store Shelves: Ingredient Label Reading for FODMAP Safety
Navigating grocery store black bean products requires vigilant label reading, as many contain hidden high-FODMAP ingredients that can trigger digestive symptoms. The safest approach focuses on simple, clean-label options with minimal additives.
| Ingredient | FODMAP Risk | Gourmend-Approved Alternative |
|---|---|---|
| Onion powder/extract | High | Chive sprigs |
| Garlic powder/extract | High | Garlic-chive stems |
| Natural flavoring | Unknown | Green leek tops |
| High fructose corn syrup | High | Maple syrup (small amounts) |
Safe Label Checklist: Look for canned black beans with only water, salt, and citric acid listed. Avoid products mentioning "spices," "natural flavors," or any form of onion/garlic derivatives. For reliable flavor enhancement, reach for your Gourmend shelf-stable broth carton instead of pre-seasoned varieties.
Organic options often feature cleaner ingredient panels, but always verify the complete ingredient list rather than relying on front-of-package claims. When in doubt, choose the simplest product available and build flavor using low FODMAP techniques at home.
Decoding Black Bean Paste, Sauce, and Fermented Beans: FODMAP Content & Culinary Use
Black bean products beyond whole canned beans present unique FODMAP challenges due to concentrated ingredients and fermentation processes. Understanding these differences helps you make informed choices for gut-friendly cooking.
Black Bean Paste: Typically contains high-FODMAP garlic and onion as primary flavor components, making it unsuitable for sensitive digestion. The concentrated nature means even small amounts exceed safe thresholds.
Black Bean Sauce: Often includes wheat-based thickeners and fermented elements that increase FODMAP load. Commercial varieties frequently contain multiple trigger ingredients in a single product.
Fermented Black Beans: While fermentation can reduce some FODMAPs, the salt-curing process concentrates flavors, requiring extremely small portions that limit practical use.
| Product Type | FODMAP Risk | Safe Serving | Gourmend Alternative |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black bean paste | High | None recommended | Homemade with chive sprigs |
| Black bean sauce | High | 1 teaspoon maximum | Gourmend broth-based sauce |
| Fermented black beans | Moderate | 1 teaspoon | Fresh beans + green leek tops |
Create FODMAP-friendly alternatives by combining your 2-tablespoon portion of canned black beans with Gourmend shelf-stable broth carton and garlic-chive stems for depth. This approach delivers authentic flavor profiles while maintaining digestive comfort.
If you're interested in learning about other legumes, you may want to read about are green beans low FODMAP for additional guidance.
Troubleshooting, What If Black Beans Cause IBS Symptoms? Solutions and Alternatives

Even with careful portion control, some individuals may experience digestive discomfort from black beans. Recognizing symptoms early and adjusting your approach prevents ongoing issues while maintaining nutritional variety.
Immediate Response Steps:
- Reduce portion size: Try 1 tablespoon instead of 2 for your next meal
- Increase rinsing time: Rinse canned beans for 60 seconds instead of 30
- Space out consumption: Allow 2-3 days between black bean meals
- Check other FODMAPs: Ensure you're not stacking multiple FODMAP sources in one meal
If symptoms persist, transition to more digestible alternatives while maintaining protein and flavor goals. Green lentils offer similar earthiness at ¼ cup serving, while edamame provides the largest safe portion at ½ cup.
Rescue Strategy: Replace black bean flavor using chive sprigs and green leek tops simmered in Gourmend shelf-stable broth carton. This combination delivers the savory depth you're craving without FODMAP triggers.
Consider meal timing and composition, consuming black beans with easily digestible carbohydrates like rice or quinoa may improve tolerance compared to pairing with other fiber-rich foods. Individual tolerance varies, so track your responses to identify your personal threshold.
For more inspiration on meal planning, check out our low FODMAP recipes for creative ways to enjoy a variety of gut-friendly dishes.
For a scientific perspective on FODMAPs and digestive health, see this comprehensive review of FODMAPs and IBS.
Final Recommendations for the Flavor-First, Low FODMAP Black Bean Experience
Successfully incorporating black beans into a low FODMAP lifestyle requires precision, quality ingredients, and strategic flavor building. The question "are black beans low fodmap" has a clear answer: yes, when limited to 2 tablespoons of properly prepared canned beans per serving.
Our Top 5 Takeaways for Confident Black Bean Enjoyment:
- Measure precisely: 2 tablespoons (40g) of rinsed, canned black beans per meal maximum
- Choose canned over dried: Processing reduces FODMAP content naturally
- Build flavor strategically: Use chive sprigs, green leek tops, and Gourmend broths for depth
- Rinse thoroughly: Remove excess starches and oligosaccharides before cooking
- Monitor individual tolerance: Start smaller and adjust based on your digestive response
Transform your black bean cooking with Gourmend shelf-stable broth carton as your flavor foundation. Our broths provide the umami depth that makes small portions of black beans taste abundant and satisfying, supporting your gut health goals without sacrificing culinary excitement.
For additional low FODMAP recipe inspiration and portion guidance, explore our comprehensive recipe library and conversion tool. Remember, the low FODMAP approach should feel empowering, not restrictive, with the right techniques and quality ingredients, you can enjoy bold, gourmet flavors while honoring your digestive needs.
To further expand your knowledge, you might also enjoy reading about are blueberries low FODMAP and how other fruits fit into a gut-friendly diet.
For more in-depth information on FODMAPs, see this detailed FODMAP resource from the University of Virginia.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are FODMAPs and why do they affect the digestion of black beans?
FODMAPs are short-chain carbohydrates that resist digestion in the small intestine and ferment rapidly in the colon, producing gas and drawing water into the intestines. Black beans contain galacto-oligosaccharides (GOS), a type of FODMAP that can cause bloating and discomfort for sensitive digestion when consumed in typical servings.
Are black beans considered low FODMAP, and what serving sizes are safe for people with IBS?
Black beans are high FODMAP in typical servings but can be low FODMAP when eaten in small portions, about 1/4 cup cooked. Research from Monash University shows canned black beans remain low FODMAP at servings up to 1/4 cup, making them safe for many people with IBS within this limit.
How can I prepare black beans to minimize FODMAP content and reduce digestive discomfort?
To reduce FODMAP content, rinse canned black beans thoroughly to remove excess oligosaccharides and limit portion sizes to about 1/4 cup cooked. Cooking dried black beans with multiple water changes and soaking can also help lower FODMAP levels and improve digestibility.
What nutritional benefits do black beans offer within low FODMAP serving limits?
Within low FODMAP serving sizes, black beans provide a rich source of plant protein, fiber, folate, magnesium, and iron. They also contain antioxidants like anthocyanins, supporting heart health and stable blood sugar while being gentle on digestion when enjoyed in controlled portions.