Is Feta Low FODMAP? Science-Based Serving Tips

Key Takeaways
- Feta cheese is low FODMAP when consumed in servings up to 40 grams, as it contains minimal lactose below the 1 gram threshold.
- Portion control is essential; starting with 20 grams can help assess individual tolerance to feta cheese.
- Choosing feta varieties with less than 1 gram of sugar per serving and avoiding those with added whey or milk solids ensures lower FODMAP content.
- Aged feta made from sheep or goat milk typically has lower lactose due to longer fermentation, but label reading is more reliable than milk source assumptions.
- Pairing feta with low FODMAP flavor substitutes like chive sprigs, scallion greens, and garlic-infused oil enhances taste without digestive discomfort.
Table of Contents
- Quick Answer, Is Feta Cheese Low FODMAP?
- Understanding the Low FODMAP Diet: Flavor Without Discomfort
- The Science of Cheese & FODMAPs, Why Feta Is (Sometimes) Safe
- How to Choose & Use Low FODMAP Feta: A Gourmet Approach
- Comparing Feta to Other Cheeses: FODMAP & Digestion
- Best Low FODMAP Cheeses for Bold Flavor
- Best of the Best, Low FODMAP Cheeses for Bold Flavor
- Troubleshooting & Solutions: Navigating Cheese Successfully
Understanding the Low FODMAP Diet: Flavor Without Discomfort
What are FODMAPs, and Why Do They Matter for IBS?
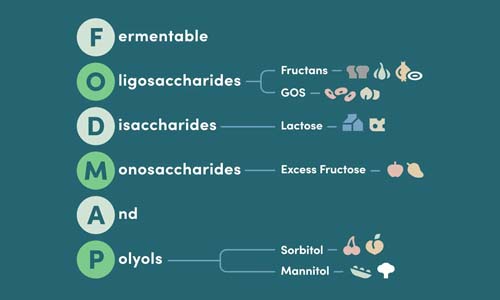
FODMAPs are fermentable carbohydrates that draw water into the intestine and produce gas when bacteria break them down. The acronym covers Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols, with lactose being the primary disaccharide in dairy products. For people with IBS, these compounds trigger bloating, cramping, and digestive discomfort because their small intestine struggles to absorb them efficiently.
Lactose becomes problematic when cheese contains more than 1g per serving. Fresh cheeses like ricotta retain higher lactose levels, while aged varieties like feta undergo fermentation that naturally reduces lactose content, making is feta low fodmap a qualified "yes" with proper portioning.
The low FODMAP approach reduces digestive discomfort without eliminating entire food groups, it's about smart portioning, not dairy-free restriction. Every ingredient has a threshold: below the limit, it's digestively gentle; above it, symptoms may occur. This principle transforms how we think about cheese, allowing feta enjoyment within safe parameters.
The flavor-first mindset recognizes that low FODMAP eating can be gourmet and satisfying. Rather than focusing on restrictions, we emphasize abundance through strategic ingredient choices, like Gourmend's broths that deliver rich, onion-garlic depth using digestively-friendly alternatives.
Essential Low FODMAP Cooking Substitutes
Gourmend broths achieve complex flavor using chive sprigs, scallion greens, leek tops, nori seaweed, and oyster mushrooms, ingredients that provide umami depth without FODMAP load. This approach proves that fodmap feta cheese dishes can be both safe and sophisticated.
Key substitution strategies:
• Replace onions with chive sprigs or green leek tops
• Swap garlic cloves with garlic-chive stems or garlic-infused oil
• Use scallion greens instead of white bulb portions
• Add nori and oyster mushrooms for umami complexity
The "abundant, gourmet" perspective prioritizes what you can enjoy rather than dwelling on limitations. When feta combines with these flavor-building ingredients, the result is Mediterranean richness that supports digestive wellness.
The Science of Cheese & FODMAPs, Why Feta Is (Sometimes) Safe

Lactose Content: The Key Metric
Lactose serves as the primary FODMAP in cheese, making its measurement crucial for digestive tolerance. During feta production, bacterial fermentation converts milk sugars into lactic acid, reducing lactose content to approximately 0.2-0.8g per 40g serving, well below the 1g threshold that typically triggers IBS symptoms.
| Cheese Type | Lactose per 40g | FODMAP Status |
|---|---|---|
| Feta | 0.2-0.8g | Low FODMAP |
| Cheddar (aged) | 0.1-0.4g | Low FODMAP |
| Ricotta | 1.2-2.0g | Moderate (limit portions) |
| Goat cheese | 0.3-0.9g | Low FODMAP |
Manufacturing & Milk Source Impacts
Sheep and goat milk feta often contains slightly lower lactose than cow milk varieties, though individual brand variation exceeds species differences. Traditional barrel-aged feta undergoes longer fermentation than mass-produced versions, resulting in more complete lactose breakdown. However, manufacturing processes vary significantly, making label reading more reliable than milk source assumptions.
Practical selection tips:
How to Choose & Use Low FODMAP Feta: A Gourmet Approach
Reading Cheese Labels for FODMAP Safety
Smart feta selection starts with the nutrition facts panel. Look for products listing less than 1 gram of sugar per serving, this indicates minimal lactose content. Avoid fetas with added whey powder or milk solids, which increase FODMAP load.
Ingredient lists reveal hidden triggers. Skip any feta containing garlic, onions, or shallots in herb blends. Traditional feta should list only milk, salt, cultures, and rennet. Mediterranean-style fetas often include herbs like oregano or thyme, perfectly safe additions that enhance flavor without digestive consequences.
Portioning Feta for Daily Meals
A 40-gram serving equals roughly 2 tablespoons of crumbled feta or a 1-inch cube. Use a kitchen scale initially to calibrate your eye, this portion provides satisfying saltiness without exceeding FODMAP thresholds.
Quick Portion Guide:
- Breakfast omelet: 20g feta + chive sprigs
- Lunch salad: 30g feta + cucumber + olive oil
- Dinner grain bowl: 25g feta + quinoa + roasted vegetables
Culinary Success with Low FODMAP Feta
Maximize feta's impact through strategic pairing. Garlic-infused olive oil amplifies the cheese's Mediterranean character, while fresh herbs like basil and oregano add aromatic depth. Lemon zest brightens feta's saltiness, creating complex flavor profiles that satisfy gourmet expectations.
Our Gourmend customers frequently combine feta with our vegetable broth in grain-based dishes, where the broth's umami from nori and oyster mushrooms complements feta's tang. This approach delivers restaurant-quality depth while maintaining digestive comfort.
For more inspiration on how to enjoy feta in creative, IBS-friendly ways, explore our collection of low fodmap recipes.
Comparing Feta to Other Cheeses: FODMAP & Digestion
Feta vs. Cheddar, Which Is Gentler?
Both feta and aged cheddar qualify as low FODMAP at standard servings, but their lactose profiles differ slightly. Aged cheddar (6+ months) contains virtually no lactose due to extended fermentation, making it exceptionally gentle for sensitive individuals. Feta typically contains 0.1-0.5g lactose per 40g serving.
| Cheese Type | Lactose Content (per 40g) | FODMAP Rating | Best Uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feta | 0.1-0.5g | Low at 40g | Salads, Mediterranean dishes |
| Aged Cheddar | <0.1g | Low at 40g+ | Melting, snacking |
| Goat Cheese | 0.2-0.8g | Low at 40g | Spreading, cooking |
Feta vs. Ricotta, What to Watch Out For
Ricotta poses greater FODMAP risk than feta due to minimal aging and higher moisture content. While feta allows 40g servings, ricotta becomes problematic above 40g, with some individuals experiencing symptoms at smaller portions. The manufacturing difference explains this gap, ricotta's fresh production preserves more lactose than feta's brining process.
Choose feta when recipes call for crumbly texture and tangy flavor. Reserve ricotta for dishes where you can control portions precisely, such as small dollops in grain bowls or measured amounts in baked dishes.
Feta vs. Dairy-Free Alternatives
Plant-based fetas vary dramatically in FODMAP content depending on base ingredients. Coconut-based versions typically remain low FODMAP, while those using cashews or almonds may trigger symptoms in sensitive individuals due to higher FODMAP nuts.
Read labels carefully for problematic starches like inulin or chicory root fiber, common thickeners that significantly increase FODMAP load. Quality vegan fetas list coconut oil, potato starch, and sea salt as primary ingredients, mimicking traditional feta's clean profile while remaining digestively gentle.
For a delicious main course that pairs beautifully with feta, try our low fodmap miso salmon recipe.
Best Low FODMAP Cheeses for Bold Flavor

Feta as a Mediterranean Powerhouse
Feta delivers unmatched versatility in low FODMAP cooking, providing sharp saltiness that elevates simple ingredients. Its crumbly texture distributes evenly through grain salads, while its tangy profile cuts through rich dishes made with Gourmend broths. This balance makes feta indispensable for creating satisfying, restaurant-quality meals at home.
Best of the Best, Low FODMAP Cheeses for Bold Flavor
Feta as a Mediterranean Highlight
Feta delivers unmatched Mediterranean punch in low FODMAP cooking. Its sharp, briny character transforms simple ingredients into restaurant-quality dishes. Is feta low FODMAP? Yes, at 40-gram servings, making it our go-to for adding complexity without digestive compromise.
Top 5 uses for feta in low FODMAP recipes:
- Grain bowls: Crumble over quinoa with roasted vegetables
- Herb salads: Pair with fresh basil and cherry tomatoes
- Stuffed peppers: Mix with rice and chive sprigs
- Flatbreads: Top with garlic-infused oil and oregano
- Omelet filling: Combine with spinach and fresh herbs
Champion Low FODMAP Cheeses for Gourmet Results
These cheeses consistently deliver flavor without triggering IBS symptoms:
- Aged Cheddar: Sharp, nutty profile perfect for melting. Safe at standard servings.
- Gouda: Sweet, caramel notes enhance soups made with Gourmend broths.
- Brie: Creamy texture ideal for appetizers with rice crackers.
- Parmesan: Umami powerhouse that amplifies savory dishes.
- Swiss: Mild, versatile option for sandwiches and melts.
- Goat Cheese: Tangy alternative to cream cheese (40g max).
- Pecorino: Salty intensity perfect for pasta dishes.
- Camembert: Rich, earthy flavor for special occasions.
Best Dairy-Free Feta for Low FODMAP Diets
Quality vegan fetas use coconut oil or potato starch bases, avoiding high-FODMAP ingredients like inulin or chicory root. Look for simple ingredient lists with recognizable components.
Safe plant-based feta characteristics:
- Coconut oil or cashew base
- No garlic or onion powder
- Minimal added starches
- Clean herb seasonings only
| Cheese Type | Safe Serving | Flavor Profile | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feta | 40g | Briny, sharp | Salads, grain bowls |
| Aged Cheddar | Standard serving | Sharp, nutty | Melting, snacking |
| Goat Cheese | 40g | Tangy, creamy | Spreads, cooking |
| Parmesan | Standard serving | Umami, nutty | Grating, finishing |
For a comforting side dish that pairs well with feta, try our low fodmap crisp roasted baby potatoes.
Troubleshooting & Solutions: Navigating Cheese Successfully
If Feta Triggers Symptoms, Strategic Next Steps
Symptoms after eating feta typically indicate portion size issues, brand variations, or individual lactose thresholds. The solution involves systematic adjustment rather than complete elimination.
Stepwise troubleshooting approach:
- Halve your portion: Try 20g instead of 40g
- Switch brands: Choose traditional sheep/goat milk varieties
- Test timing: Eat feta with other foods, not alone
- Consider alternatives: Move to aged cheddar or goat cheese
Avoiding Common Low FODMAP Cheese Mistakes
Most cheese-related symptoms stem from preventable errors in selection and portioning.
Critical action steps:
- Weigh your cheese: Eyeballing portions leads to overconsumption
- Read every ingredient list: Hidden garlic and onion powder appear frequently
- Introduce one cheese at a time: Test tolerance systematically
- Account for cumulative lactose: Multiple dairy servings add up
For a convenient way to stock your kitchen with FODMAP-friendly essentials, consider the Low FODMAP Pantry Starter Bundle (Garlic Lover Edition).
For further reading on FODMAPs and IBS, see this external resource.
Dining Out, Enjoying Feta Safely
When dining out, ask about cheese ingredients and portion sizes. Request feta on the side, and pair with low FODMAP accompaniments like cucumber, tomatoes, and olive oil. If in doubt, skip herb blends that may contain garlic or onion powder. With a little planning, you can enjoy feta’s bold flavor without digestive discomfort, even away from home.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes feta cheese low FODMAP, and how important is portion control when consuming it?
Feta cheese is low FODMAP because it contains minimal lactose, typically under 1 gram per 40-gram serving, which keeps it gentle on digestion. Portion control is essential, starting with smaller amounts like 20 grams helps you assess your personal tolerance and enjoy feta without discomfort.
How can I identify low FODMAP feta cheese varieties when shopping?
Look for feta cheeses with less than 1 gram of sugar per serving and avoid those with added whey or milk solids, as these can increase FODMAP content. Reading labels carefully is key, since lactose levels vary more reliably by ingredient list than by milk source alone.
What are some effective low FODMAP substitutes to enhance the flavor of dishes containing feta cheese?
Pair feta with low FODMAP flavor boosters like chive sprigs, scallion greens, or garlic-infused oil to add depth without digestive discomfort. These ingredients provide onion-like richness that complements feta’s tangy profile while keeping dishes gut-friendly.
Why does aged feta cheese typically have lower lactose levels compared to fresh cheeses?
Aged feta undergoes longer fermentation, during which bacteria break down lactose, reducing its content naturally. This process makes aged feta easier to digest compared to fresh cheeses that retain higher lactose levels.